Understanding the THCA to THC Conversion Rate: A Practical Guide
Introduction to Cannabis and THC
THC is recognized as the primary psychoactive compound, being the compound found in cannabis plants that is responsible for the psychoactive effects associated with cannabis use. The cannabis plant contains various cannabinoids, including THCA, which is the non psychoactive precursor to THC and impacts thc values.
- Introduction to Cannabis and THC
- What is THCA?
- What is THC?
- THCA vs. THC
- Decarboxylation Explained
- Why Decarboxylation Matters
- Factors That Influence THC Conversion
- Ideal Temperature for Decarboxylation
- Ideal Time for Decarboxylation
- Lab Testing and THC Content
- THC Content Calculation Formula
- Real-World Example of Conversion
- Total THC vs. THC
- THCA in Raw Cannabis
- Effects of THC
- Health Benefits of THCA
- THCA in Edibles and Oils
- Storing Cannabis for Maximum Potency
- THC Loss During Processing
- Popular THCA-Rich Strains
- THC Conversion and Cannabis Concentrates
- Consumption Methods and Conversion
- DIY Decarboxylation at Home
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What is the THCA to THC conversion rate?
- Why is the conversion rate not 100%?
- Does eating raw cannabis get you high?
- Can you decarboxylate THCA without heat?
- How long does decarboxylation take?
- What happens if you over-decarboxylate cannabis?
- How is total THC calculated in lab tests?
- Is THCA legal in the U.S.?
- Why is THCA preferred in some medical products?
- Can I convert THCA to THC at home?
Understanding the relationship between THCA and THC is essential for navigating the cannabis industry and making informed decisions about cannabis products to achieve the desired effects. The thca to thc conversion rate is a critical factor in determining the efficient conversion and desired potency levels of cannabis products.
What is THCA?
THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid found in the raw cannabis plant, including dry cannabis flower and live cannabis plants, where precise temperature control is vital.
It is the acidic precursor to THC, and not all thca converts; meaning it must undergo decarboxylation to convert into active THC.THCA is present in high concentrations in fresh cannabis flower before any heat or processing is applied. Many cannabis users consume THCA for its potential anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective benefits.
What is THC?
THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) is the psychoactive compound where thc levels are present and responsible for the “high” associated with cannabis. It interacts with CB1 receptors in the brain and central nervous system.
THC provides a range of therapeutic benefits, including pain relief, appetite stimulation, and mood enhancement, contributing to the final thc yield. The psychoactive effects of THC vary depending on the dose, strain, and user sensitivity.
THCA vs. THC
THCA is non-psychoactive, while THC produces psychoactive effects by binding to cannabinoid receptors. THCA must undergo decarboxylation for effective thca conversion to transform into THC and become psychoactive. Each cannabinoid has unique potential health benefits and applications. Consumers often choose between raw THCA and decarboxylated THC products depending on their needs.
Decarboxylation Explained
Decarboxylation is the chemical process that removes a carboxyl group from THCA, transforming it into THC. This process requires heat, which triggers a molecular change.
The decarboxylation process is essential for activating THC in cannabis for recreational or medicinal use. Without decarboxylation, to achieve efficient converting thca of how much thca converts, cannabis products remain largely non-psychoactive.
Why Decarboxylation Matters
Proper decarboxylation ensures that users experience the full effects of THC. Inaccurate decarboxylation can result in varying thca percentages underwhelming potency.
The cannabis industry relies on precise decarboxylation to maintain product consistency. Cannabis users must understand decarboxylation to dose effectively.
Factors That Influence THC Conversion
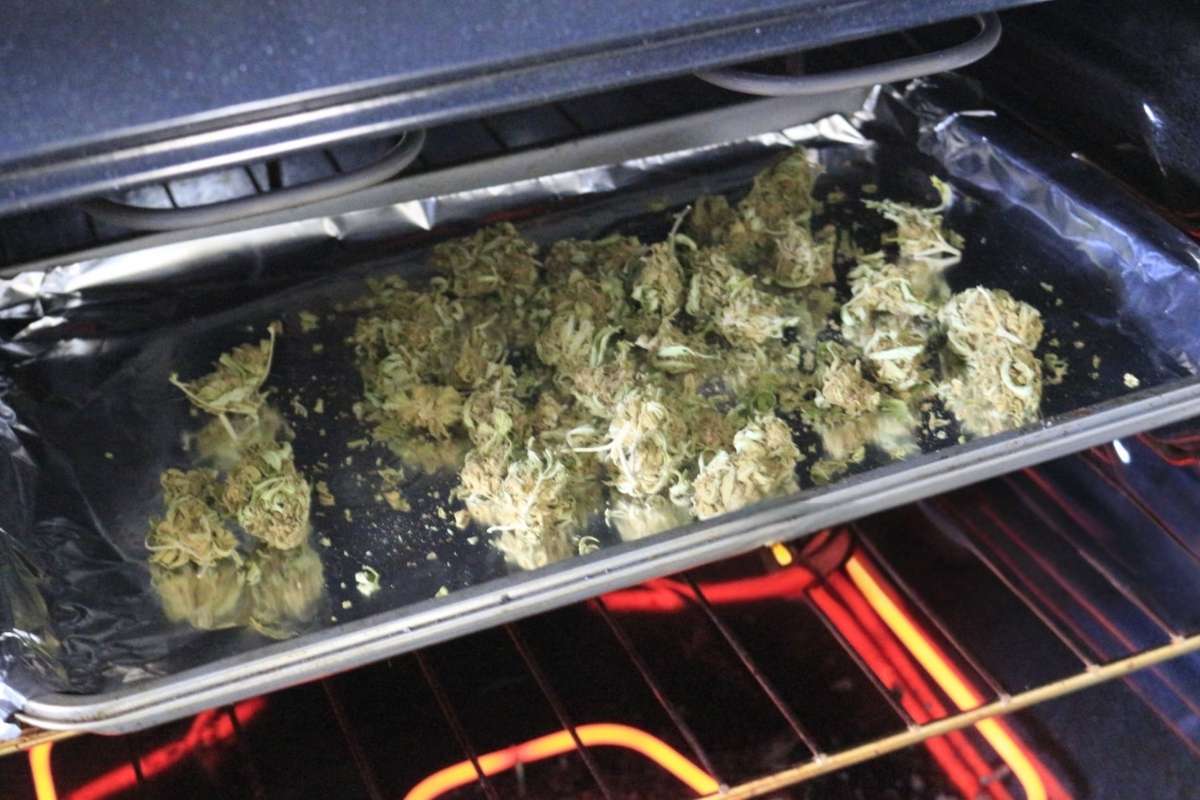

Several factors affect how efficiently THCA converts to THC, including the conversion factor. Temperature and time are the most significant variables in the decarboxylation process.
Material quality also plays a role, as well as the presence of cannabinoid acids and other compounds. Environmental factors during storage and handling can affect conversion potential.
Ideal Temperature for Decarboxylation
The optimal temperature for converting THCA to THC is between 220°F and 240°F (104°C to 115°C). Too low a temperature may result in incomplete conversion. Excessively high temperatures can degrade THC and other cannabinoids. Ovens, toaster ovens, or specialized decarboxylation machines can be used.
Ideal Time for Decarboxylation
Time is just as crucial as temperature in the decarboxylation process.Generally, cannabis is decarboxylated at 230°F for 30-45 minutes.Time may vary based on moisture content, oven efficiency, and strain composition. Over-decarboxylation can destroy cannabinoids, reducing potency.
Lab Testing and THC Content
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Lab Testing Method | High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) – preferred as it measures both THCA and THC without heat. |
| Other Testing Method | Gas Chromatography (GC) – uses heat, so THCA is automatically converted to THC during testing. |
| Conversion Process | Decarboxylation – heating cannabis (usually at 220–250°F for 30–45 mins) converts THCA into psychoactive THC. |
| Conversion Formula | THC = THCA × 0.877 (due to molecular weight loss of CO₂ during decarboxylation). |
| Typical THCA Content | Raw cannabis flowers can have 15%–25% THCA before decarboxylation. |
| Typical THC Content (Post-Conversion) | After full conversion, expect 13%–22% THC, depending on original THCA content and efficiency of the process. |
| Factors Affecting THC Yield | Temperature, duration, moisture content, and quality of the cannabis strain. |
| Why Testing Matters | Ensures accurate potency labeling, consumer safety, legal compliance, and helps medical users dose properly. |
THC content, along with cannabidiolic acid, is typically measured through lab testing to ensure product quality. Lab results often show total THC, including both THCA and active THC. Accurate lab testing is essential for regulatory compliance and consumer trust. Understanding lab results helps users determine product potency.
THC Content Calculation Formula
To estimate THC yield from THCA, especially for calculating THC to thc content the following formula is used: THC = (%THCA) x 0.877 + (%THC). The factor 0.877 accounts for the molecular weight difference after decarboxylation. This formula gives a more realistic picture of total available THC in a product.
Real-World Example of Conversion
Let’s say a cannabis flower contains 20% THCA and a corresponding thc percentage of 1% THC. Using the formula: (20 x 0.877) + 1 = 18.54% total THC.
This example illustrates how raw THCA contributes significantly to THC content after decarboxylation. Understanding this helps users gauge the potential thc of how much thc their dosage should be.
Total THC vs. THC

Total THC includes the potential THC yield from THCA after decarboxylation. It provides a more comprehensive understanding of a product’s potency. Knowing both active THC and total THC is vital for accurate dosing. Labels often distinguish between THC and total THC for this reason.
THCA in Raw Cannabis
Raw cannabis, such as freshly harvested flower, contains mostly tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) and other valuable cannabinoids. It has negligible amounts of THC unless heated.
Raw cannabis is often used in juicing or cold-pressed applications.THCA in raw form may offer anti-inflammatory or anti-nausea effects without intoxication.
Effects of THC
THC affects the endocannabinoid system by binding to CB1 receptors, influencing one’s cannabis journey. It can produce feelings of euphoria, relaxation, altered perception, and increased appetite.
Medicinally, THC, along with thca and thc percentages, is used for chronic pain, glaucoma, PTSD, and more. Side effects can include dry mouth, anxiety, and impaired memory in some users, affecting their overall cannabis experience.
Health Benefits of THCA
| Health Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Anti-Inflammatory | THCA may help reduce inflammation, making it potentially useful for conditions like arthritis and autoimmune disorders. |
| Neuroprotective Effects | Early research suggests THCA may protect brain cells, potentially helping with neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. |
| Anti-Nausea | THCA may reduce nausea and vomiting, especially in cases related to chemotherapy or chronic illness. |
| Antioxidant Properties | Acts as a powerful antioxidant, helping protect cells from oxidative stress and damage. |
| Appetite Stimulation | May naturally stimulate appetite, useful for people with eating disorders or undergoing medical treatments. |
| Anti-Proliferative | Some studies suggest THCA might inhibit the growth of certain cancer cells (more research needed). |
| Muscle Spasms Relief | THCA may help reduce muscle spasms and cramps, useful for conditions like multiple sclerosis. |
| Pain Relief | Though not as strong as THC, THCA may provide mild analgesic effects without intoxication. |
THCA has shown potential benefits in preliminary research, particularly related to its thca and thc content. It may offer anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and anti-proliferative properties. THCA is being explored for its role in managing arthritis, epilepsy, and neurodegenerative diseases. Since it does not cause a high, it is preferred by some medical users.
THCA in Edibles and Oils
THCA can be included in various cannabis products like raw tinctures, oils, and capsules.To retain its acidic form, these products must avoid heat during processing.
They are used by patients seeking benefits without psychoactive effects, particularly when avoiding heating cannabis. Proper labeling is key to avoiding unintentional intoxication.
Storing Cannabis for Maximum Potency

Storage conditions significantly impact the stability of THCA and cannabis products containing THC. Cannabis should be kept in a cool, dark, airtight environment.
Light, oxygen, and heat exposure can degrade cannabinoids over time, impacting their effectiveness, which is often measured by liquid chromatography. Vacuum-sealed containers and humidity packs help maintain freshness.
THC Loss During Processing
THC can degrade during extraction, cooking, or storage if not handled properly. Improper processing may lead to lower than expected THC content. Consistent lab testing cannabis and quality control are crucial for determining the conversion rate and accuracy. Manufacturers strive for complete conversion to maintain THC content through controlled environments.
Popular THCA-Rich Strains
Some cannabis strains are naturally high in THCA. Examples include Mimosa, Ice Cream Cake, and White Runtz. These strains are popular among those seeking high potency after decarboxylation. Knowing the THCA content of strains helps with product selection.
THC Conversion and Cannabis Concentrates
Cannabis concentrates like shatter, wax, and live resin also contain THCA, undergoing converting thca to produce active THC. These products must undergo converting thca through decarboxylation before or during consumption. Concentrates offer high THC yields due to dense cannabinoid profiles. They require careful handling and dosing.
Consumption Methods and Conversion
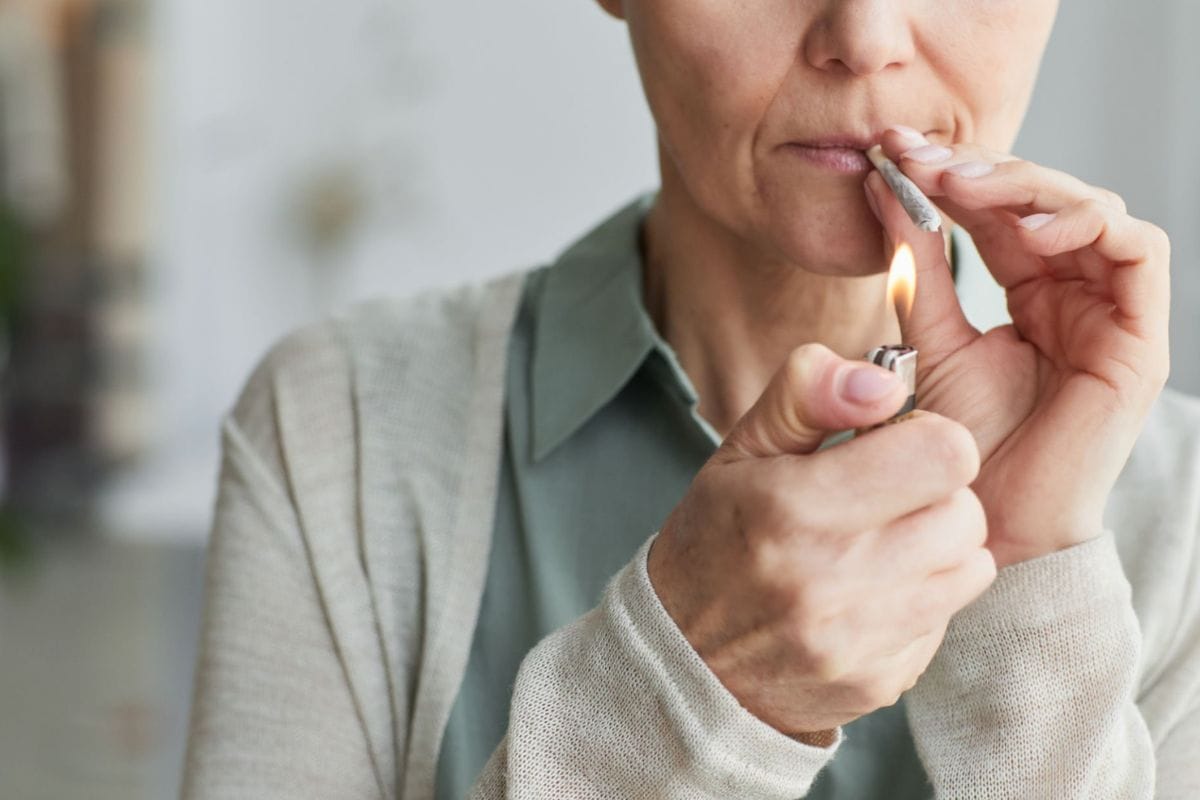

Each consumption method affects how efficiently THCA is converted in the conversion process. Smoking and vaporizing instantly decarboxylate THCA. Ingesting raw cannabis retains THCA, while edibles require baking (decarbing). Knowing how you consume affects how much active THC you receive.
DIY Decarboxylation at Home
Home users can decarboxylate cannabis using ovens or specialized devices. Ensure even heating and avoid burning by using baking sheets and parchment paper. Use an oven thermometer for temperature accuracy when baking cannabis. Always store decarboxylated cannabis in airtight containers.
Conclusion
Understanding thc’s molecular weight in relation to the thca to thc conversion rate and the chemical reaction in the conversion process need for precise heat exposure and temperature control is essential for anyone using cannabis. Decarboxylation is a vital step in unlocking the psychoactive potential of cannabis. By managing temperature, time, and quality in this chemical reaction , users can maximize THC yield. As the cannabis industry grows, so does the need for education on proper conversion techniques.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the THCA to THC conversion rate?
The conversion rate is approximately 87.7%, meaning that when THCA is heated and decarboxylated, it turns into THC at a ratio of THCA × 0.877. This accounts for the loss of a carboxyl group (CO₂) during the process.
Why is the conversion rate not 100%?
The rate is less than 100% because the carboxyl group is removed during decarboxylation, resulting in a lighter molecule. Additionally, some THC may degrade into CBN or other compounds if exposed to excessive heat or time.
Does eating raw cannabis get you high?
No. Raw cannabis primarily contains THCA, which is non-psychoactive. Without heating or decarboxylation, it won’t produce the high typically associated with THC.
Can you decarboxylate THCA without heat?
Technically, yes—over time, THCA can convert to THC through natural aging (light and air exposure), but this is slow and inefficient compared to heat-based methods.
How long does decarboxylation take?
For dried cannabis flower, 30 to 45 minutes at 240°F (115°C) is a common recommendation. However, time and temperature can vary depending on the material and desired outcome.
What happens if you over-decarboxylate cannabis?
Overheating or extended exposure to heat can degrade THC into CBN, which is mildly psychoactive but significantly less potent. This can lead to reduced potency and altered effects.
How is total THC calculated in lab tests?
Labs use the formula:
Total THC = (THCA × 0.877) + THC
This gives a more accurate representation of how much psychoactive THC will be present after use.
Is THCA legal in the U.S.?
THCA can be legal in some states when derived from hemp and as long as total THC remains under 0.3% by dry weight. However, once decarboxylated into THC, it may exceed legal limits, depending on local laws.
Why is THCA preferred in some medical products?
THCA is non-intoxicating and may have potential anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and anti-nausea effects. It’s often preferred by users who want therapeutic benefits without the high.
Can I convert THCA to THC at home?
Yes. Many people decarboxylate cannabis at home using an oven, slow cooker, or decarb device to prepare edibles, tinctures, or oils effectively.