THCA vs CBD: Key Differences and Their Unique Benefits Explained
Introduction to Cannabis Compounds
The hemp plant, including raw cannabis plants and thca flower, is composed of numerous active compounds called cannabinoids, which are often used in thca and cbd products. Among the most studied are THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) and CBD (cannabidiol).
Both THCA and CBD are classified as non psychoactive cannabinoids in their natural forms, which means they do not produce psychoactive effects making them essential components of medical marijuana, and they include the non psychoactive cannabinoid found in various products, offering a wide range of potential health benefits and medical benefits.
- Introduction to Cannabis Compounds
- What is THCA?
- What is CBD?
- THCA vs CBD: Molecular Structure
- Psychoactive Properties
- Health Benefits of THCA
- Health Benefits of CBD
- Entourage Effect
- Consumption Methods
- THCA in Raw Cannabis
- CBD in Hemp and Marijuana
- Extraction Techniques
- Full-Spectrum vs Isolate
- Legal Considerations
- Product Availability
- Effects on the Endocannabinoid System
- Therapeutic Potential
- Use in Pets
- Cooking with THCA and CBD
- Shelf Life and Storage
- Side Effects and Tolerability
- Drug Testing Concerns
- Popular Product Types
- Conclusion
- FAQs: THCA vs CBD
- Is THCA stronger than CBD?
- Can THCA make you high?
- Does CBD affect memory or cognition?
- Is CBD safe for daily use?
- Can I use THCA and CBD together?
- What's the best way to consume THCA?
- Are THCA products easy to find?
- Is CBD addictive?
- How long does it take for CBD to work?
- Can CBD and THCA be used in skincare?
These psychoactive cannabinoids and others interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS), influencing mood, pain, inflammation, and overall homeostasis.
Understanding these two compounds helps consumers make informed decisions about wellness and medicinal cannabis products.
What is THCA?
THCA is the acidic precursor to THC, found in fresh cannabis plants, as well as raw hemp and marijuana plants. Unlike THC, THCA does not produce a high unless it is decarboxylated (heated), which converts it into THC.
THCA exists in large quantities in live or freshly harvested cannabis. It is gaining attention for its potential anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties and effects.
What is CBD?
CBD is a non psychoactive compound that non-intoxicating cannabinoid found in both hemp and marijuana, which is often included in cbd and thca products. It is known for its calming effects and is used widely in wellness and medicinal products.
CBD, a non psychoactive compound, does not bind directly to cannabinoid receptors but influences them indirectly. This interaction results in various therapeutic effects, including stress relief and reduced inflammation.
THCA vs CBD: Molecular Structure
The key differences are that HCA and CBD have different chemical structures, which explains their unique interactions with the ECS.
THCA contains a carboxylic acid group that breaks off when exposed to heat. CBD has a stable structure that remains intact whether heated or not. These structural differences determine their bioavailability and effects.
Psychoactive Properties
THCA is non-psychoactive in its raw form, but it becomes psychoactive as THC after heating. CBD remains non-psychoactive regardless of how it is consumed. This makes CBD a preferable option for those seeking relief without intoxication. Consumers looking for a non-euphoric experience often opt for CBD-rich products.
Health Benefits of THCA
THCA may help reduce inflammation and pain due to its analgesic properties, and it is also being studied for its potential neuroprotective effects without intoxication. Preclinical studies show that THCA may also support neuroprotection and healthy digestion.
Some anecdotal evidence suggests it may help with nausea and appetite stimulation when using raw cannabis buds. Because it is non-intoxicating, it can be used during the day.
Health Benefits of CBD
| Benefit | CBD (Cannabidiol) | THCa (Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid) |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-inflammatory | Yes – widely studied for reducing inflammation | Yes – early research suggests strong anti-inflammatory properties |
| Pain relief | Yes – commonly used for chronic pain management | Yes – potential for non-psychoactive pain relief |
| Anxiety & stress relief | Yes – calming, helps with anxiety, PTSD, and general stress | Limited – not yet widely studied for anxiety |
| Neuroprotective effects | Yes – may protect brain cells, used in epilepsy treatment | Promising – may help with neurodegenerative conditions |
| Anti-seizure | Yes – FDA-approved for epilepsy (Epidiolex) | Not enough data |
| Sleep support | Yes – helps with sleep disorders and insomnia | Unclear – more studies needed |
| Appetite regulation | Mixed – may suppress or stimulate appetite | May increase appetite (non-psychoactive version of THC) |
| Anti-nausea | Limited – less effective than THC | Promising anti-nausea properties (non-intoxicating) |
| Non-psychoactive | Yes – does not get you high | Yes – raw form, non-psychoactive until heated |
| Legal status (U.S.) | Federally legal if derived from hemp (≤0.3% THC) | Legal in raw form, but heating converts it to THC, which is restricted |
CBD is widely known for its wellness benefits and medical benefits, including anti-anxiety, anti-inflammatory, and anti-seizure properties. It is used to manage epilepsy, chronic pain, insomnia, and general wellness.
CBD is also being explored for its potential in treating neurodegenerative conditions, potentially paving the way for future medical treatments. Its broad applicability makes it a favorite in both medicinal and wellness markets.
Entourage Effect
The entourage effect is the theory that cannabinoids work better together. CBD and THCA may enhance each other’s benefits when consumed in full-spectrum formulations, acting upon various cannabinoid receptors in the body.
This synergy is one reason full-spectrum extracts are often preferred over isolates. Including minor cannabinoids and terpenes can amplify therapeutic outcomes based on their molecular structure.
Consumption Methods

THCA is typically consumed raw or in minimally processed products to preserve its acidic form. Juicing raw cannabis or using THCA tinctures are common methods. CBD can be consumed through oils, capsules, edibles, topicals, and vape products. Each method affects how quickly the compound takes effect.
THCA in Raw Cannabis
THCA is abundant in live or freshly harvested cannabis. Exposure to light and heat during drying and curing reduces THCA levels as it converts to THC. Raw cannabis users often juice the leaves to get THCA without psychoactive effects. Proper storage is essential to preserve THCA content.
CBD in Hemp and Marijuana
CBD is present in both hemp and marijuana, but hemp contains higher levels, making hemp derived products a popular choice. Industrial hemp is often grown specifically for CBD extraction.
Marijuana-derived CBD may contain higher THC levels depending on the strain. Both sources are used in the production of CBD-rich products.
Extraction Techniques
| Aspect | CBD (Cannabidiol) | THCa (Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid) |
|---|---|---|
| Common Extraction Methods | – CO₂ Extraction – Ethanol Extraction – Hydrocarbon (Butane/Propane) – Lipid Infusion | – Cold-Press Extraction – Live Rosin Pressing – Solventless Ice Water Extraction |
| Purpose of Extraction | Extract CBD from hemp or cannabis for oils, tinctures, edibles | Preserve raw, acidic form (THCa) without decarboxylation |
| Temperature Sensitivity | Moderate – can tolerate mild heat | Very high – heat converts THCa to psychoactive THC |
| Solvent Use | Often involves solvents (CO₂, ethanol) | Typically solventless to preserve purity |
| Final Form | CBD Isolate, Full-spectrum oil, Broad-spectrum oil | Live Rosin, THCa Crystals, Raw Extracts |
| Preservation of Cannabinoids | High with controlled CO₂/ethanol processes | Critical – must keep raw form; heat and light can degrade it |
| Flavor & Terpene Retention | Moderate (often refined or filtered oils) | High – solventless and cold extraction retains natural plant compounds |
| Cost & Equipment | Expensive equipment but high scalability | Costly due to precision, especially for solventless methods |
| Industrial Use | Widely used in medical, wellness, cosmetics | Primarily in raw cannabis markets, concentrates, and high-end products |
| Legality Consideration | Federally legal if from hemp and under 0.3% THC | Legal as raw THCa, but heating turns it into THC (regulated substance) |
THCA is extracted using cold methods to preserve its non-decarboxylated form. CBD is extracted using CO2, ethanol, or hydrocarbon methods. Full-spectrum extracts may include both CBD and THCA along with other cannabinoids. Proper extraction ensures potency and purity.
Full-Spectrum vs Isolate
Full-spectrum products contain a range of cannabinoids, including THCA or CBD. Isolates contain only one cannabinoid and no additional plant compounds. Full-spectrum products often provide stronger and more balanced effects. However, isolates may be preferred by users needing to avoid THC altogether.
Legal Considerations
CBD derived from hemp is federally legal in the U.S. if it contains less than 0.3% THC. THCA is legal in raw form, but heating it may violate THC regulations; thus, understanding thca legal parameters is crucial.
Cannabis laws vary by state and country, affecting access to both cannabinoids. Always verify legal status before purchasing or using these products.
Product Availability
CBD products are widely available online and in retail stores. THCA products are more niche and usually found in dispensaries. Demand for raw cannabinoid formulations is increasing with public awareness. Consumers should check for third-party testing and ingredient transparency.
Effects on the Endocannabinoid System
CBD indirectly influences CB1 and CB2 receptors. THCA interacts less directly but still influences ECS signaling.Both compounds, including THCA, have potential therapeutic benefits and help regulate mood, appetite, sleep, and immune response. Their mechanisms differ but complement the ECS in unique ways.
Therapeutic Potential
CBD has documented uses for epilepsy and chronic pain. THCA is being studied for potential benefits in neuroprotection, anti-inflammatory, and digestive support, in addition to the benefits provided by cbd flower. Both show promise in managing autoimmune and neurological conditions. More research is needed to confirm long-term effects and safety.
Use in Pets
CBD is commonly used in pet wellness products. Pet owners use it to manage anxiety, arthritis, and aging-related symptoms. THCA derived from raw cannabis flowers and buds is less common in pet products but may have future applications. Always consult a healthcare provider or veterinarian before administering cannabinoids to pets.
Cooking with THCA and CBD
| Recipe | Cannabinoid Used | Purpose | Preparation Tip | Heat Sensitivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBD Smoothie | CBD | Relaxation, anti-anxiety, anti-inflammatory | Add CBD oil to your favorite fruit smoothie | No issue – no heat involved |
| THCa Raw Salad | THCa | Anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective | Use fresh cannabis leaves or THCa tincture | Must keep raw – no cooking |
| CBD Energy Balls | CBD | Stress relief, healthy snack | Mix oats, honey, peanut butter, and CBD oil | No baking – fridge only |
| THCa Juice or Shot | THCa | Detox, nausea relief | Blend raw cannabis with apple, lemon, and ginger | No heating – cold press |
| CBD Guacamole | CBD | Mood booster, inflammation relief | Add CBD oil to mashed avocado mix | No cooking required |
| THCa Yogurt Parfait | THCa | Wellness, calming effect | Layer yogurt, fruits, and raw cannabis extract | Use cold ingredients only |
| CBD Tea (Lukewarm) | CBD | Calming, helps with sleep | Brew herbal tea, cool slightly, then add CBD oil | Avoid boiling the CBD oil |
| THCa-Infused Pesto | THCa | Anti-inflammatory, raw nutrition | Blend fresh basil, garlic, nuts, olive oil & THCa | Use raw or after cooking |
CBD is stable under low heat and suitable for cooking in edibles, unlike THCA which undergoes a process called decarboxylation when heated. THCA converts to THC when heated, making it tricky for raw applications.
Raw THCA-infused foods in various thca forms require no cooking to maintain their properties. CBD products can also be added to smoothies, snacks, or baked goods for pain relief.
Shelf Life and Storage
CBD has a long shelf life when stored in a cool, dark place. THCA degrades over time, especially if exposed to heat. Refrigeration may extend the shelf life of THCA products. Proper packaging also ensures longevity and potency.
Side Effects and Tolerability
CBD is well-tolerated with few side effects, providing numerous wellness benefits such as reduced drowsiness or dry mouth. THCA has limited reported side effects due to its non-psychoactive nature. Consumers with pre-existing conditions should consult healthcare professionals. Start with low doses and gradually increase as needed.
Drug Testing Concerns
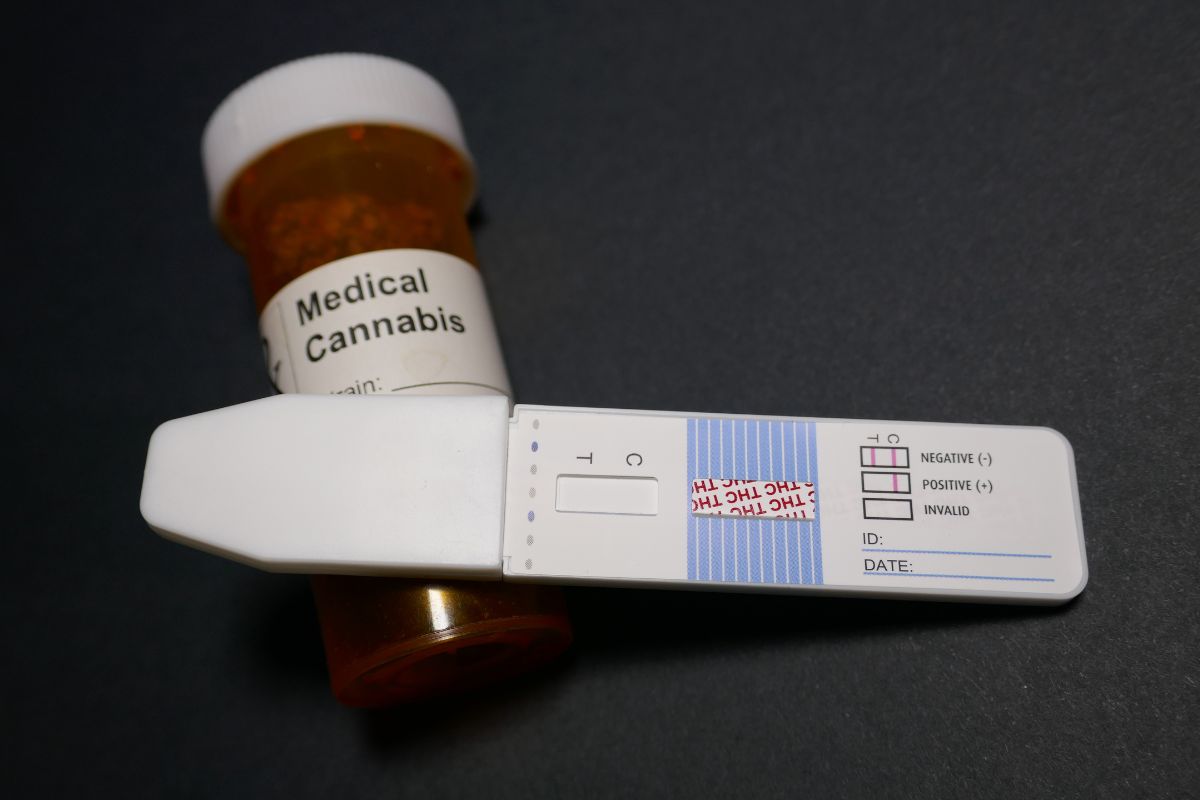
CBD usually doesn’t show up on drug tests unless contaminated with THC. THCA may convert to THC and lead to positive drug tests. Check lab reports for THC content before using these products. Choose THC-free CBD formulations if drug testing is a concern.
Popular Product Types
CBD: tinctures, gummies, capsules, vape pens, and topicals. THCA: raw tinctures, capsules, cannabis juice, and cold-pressed oils. Each product type offers unique onset times and duration of effects. Match the product form to your lifestyle and wellness goals.
Conclusion
THCA and CBD each offer distinct benefits rooted in their chemical composition and biological interaction. Whether you’re seeking relief from pain, inflammation, or stress, understanding the differences between these two cannabinoids can guide better choices.
Consider the legal status, product types, and therapeutic goals when selecting between CBD and THCA. As research continues to evolve, these compounds may reveal even more health-promoting properties in the future.
FAQs: THCA vs CBD
Is THCA stronger than CBD?
No, THCA is not stronger. They serve different purposes—THCA for raw benefits, CBD for stress and inflammation.
Can THCA make you high?
Not unless it’s heated, as heat can induce psychoactive effects. In its raw form, THCA does not produce a high.
Does CBD affect memory or cognition?
CBD does not impair memory and may support cognitive health.
Is CBD safe for daily use?
Yes, CBD is generally safe when used as directed.
Can I use THCA and CBD together?
Yes. Using them together may enhance therapeutic effects via the entourage effect.
What’s the best way to consume THCA?
Juicing raw cannabis or using cold-extracted tinctures is effective.
Are THCA products easy to find?
They are less common than CBD products and usually found in dispensaries.
Is CBD addictive?
No. CBD is not considered addictive and does not cause dependency.
How long does it take for CBD to work?
Effects vary but may be felt within 30–60 minutes for tinctures and edibles.
Can CBD and THCA be used in skincare?
Yes. Both have anti-inflammatory properties beneficial for topical use.