What is HxC Hexahydrocannabinol: A Concise Overview
HHC is the new kid on the cannabis block, taking the ordinary joe of pot and turning it into the superhero of highs. Imagine it as the cooler, beefed-up brother of delta-8-THC, with a sprinkle of science magic that makes it outshine both delta-9-THC and CBD. It’s got folks with a hunger for knowledge and a knack for discovery scrambling to peel back the layers of HHC’s mystery, eager to see how it’s going to shake things up. **Keep your eyes wide open**; you’re about to dive into a gold mine of awesome facts and the kind of know-how that’s usually kept hush-hush. Who’s this for, you ask? Anyone who gets a kick out of riding the newest wave in the cannabis world. Embarking on this HHC journey might just unlock that super chill or health vibe you’ve been on the hunt for.
In its various forms, HHC can be considered more potent than its precursor, delta-8-THC. This difference in potency is due to the extra hydrogen atoms found in HHC’s molecular structure. The scientific community is still exploring this new cannabinoid, and while some information is available, further research is needed to fully establish its properties, benefits, and potential risks.
As the world of cannabinoid research continues to expand, HHC offers a new avenue of investigation for those interested in the therapeutic and recreational possibilities of cannabis derivatives. This enigmatic compound invites us to delve deeper into the intricacies of cannabis science and uncover the potential that lies within the diverse spectrum of cannabinoids.
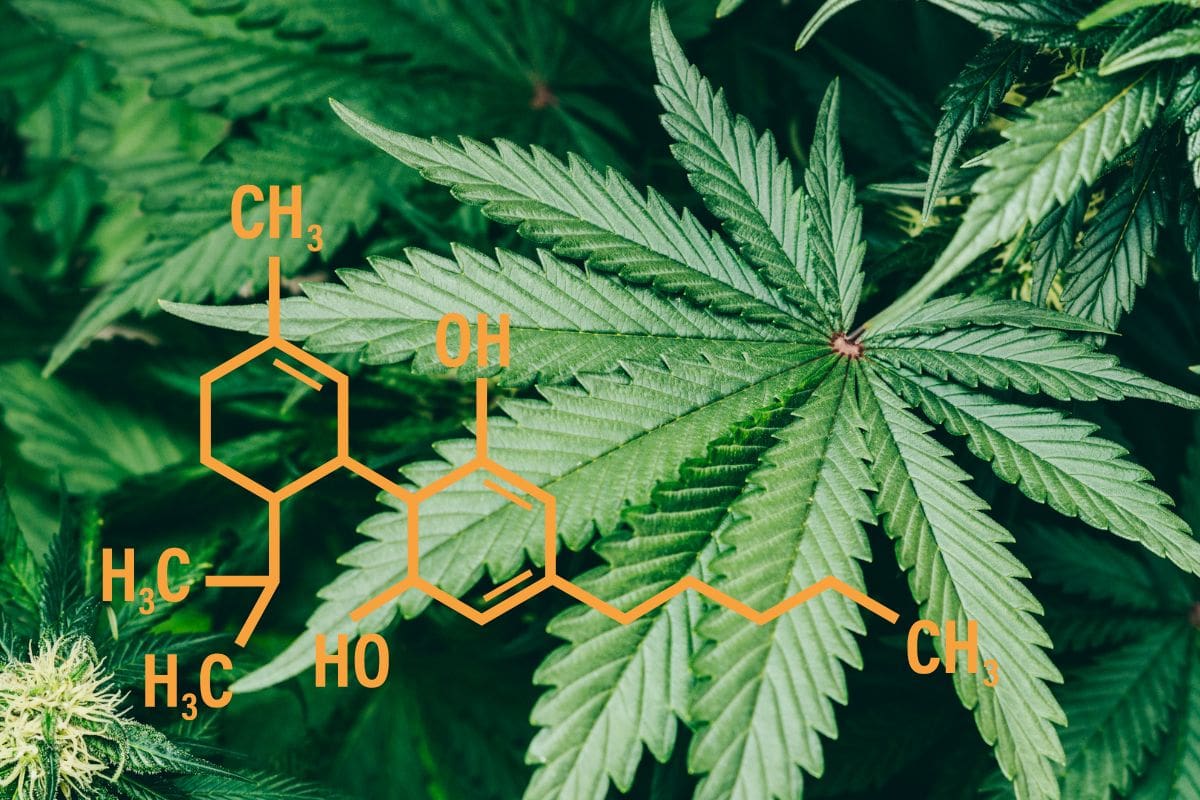
Chemical Composition of HxC Hexahydrocannabinol
Hexahydrocannabinol (HHC) is a semi-synthetic cannabinoid derived from Δ8-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ8-THC), the primary psychoactive compound found in cannabis. HHC is created by adding hydrogen atoms to the Δ8-THC structure, resulting in a hydrogenated derivative1. This process modifies the chemical composition of the compound while retaining its cannabinoid properties.
The molecular formula of HHC is C₁₉H₂₈O₂, and it has a molecular weight of 284.43 g/mol. In addition to the added hydrogen atoms, HHC shares many structural similarities with its parent compound, Δ8-THC. Both compounds have a 2-hydroxycyclohexyl moiety that gives them a cannabinoid-ring system2. However, the hydrogenation process alters the double bonds in the carbon chain, which leads to a difference in psychoactive effects and potency.
While HHC consists of multiple stereoisomers, most research and use in the market refers to unspecified mixtures of these stereoisomers1. The presence of stereoisomers means that HHC molecules may have the same chemical formula but exhibit different orientations and connections in their atomic arrangement. This variation in molecular structure contributes to the diverse range of effects and potencies observed in HHC and its derivatives.
In conclusion, HxC Hexahydrocannabinol or HHC is a semi-synthetic cannabinoid that results from the hydrogenation of Δ8-THC. Its chemical composition includes extra hydrogen atoms, leading to a molecular formula of C₁₉H₂₈O₂. The molecule shares structural similarities with Δ8-THC but displays different effects and potencies due to its altered chemical structure and the presence of stereoisomers.

Biosynthesis and Natural Occurrence
Hexahydrocannabinol (HHC) is a semi-synthetic cannabinoid derived from the cannabis plant. Unlike naturally occurring cannabinoids such as THC and CBD, HHC is synthesized through a process that involves adding extra hydrogen atoms to the molecular structure of THC. This modification results in a compound with similar cannabimimetic properties but potentially different pharmacological effects1.
In the cannabis plant, the biosynthesis of cannabinoids like THC and CBD occurs through a series of enzymatic reactions. These reactions involve the conversion of precursor molecules like olivetolic acid and geranyl pyrophosphate into various cannabinoids. However, HHC is not a naturally occurring cannabinoid in the plant, so it doesn’t follow the same biosynthetic pathways2. Instead, HHC is synthesized through chemical alterations of the naturally occurring molecules, which introduces extra hydrogen atoms into their structure.
Although HHC emerged on the drug market in 2021, its synthesis and cannabimimetic activity were first studied and reported in the scientific literature1. As a semi-synthetic cannabinoid, HHC is produced through laboratory modifications rather than directly extracted from the cannabis plant.
Due to its recent appearance, there is limited information on the natural occurrence of HHC in the environment. Moreover, since it is a semi-synthetic compound, it is highly unlikely to be found in significant quantities in nature. Instead, HHC is predominantly encountered as a drug substance with potential therapeutic applications or as a recreational drug in various forms, including vape cartridges, concentrates, and edibles. Further research is required to explore the distribution, prevalence, and potential medical benefits of this emerging cannabinoid.
Pharmacological Effects of HxC Hexahydrocannabinol
Hexahydrocannabinol (HxC) is a semi-synthetic cannabinoid that first appeared on the drug market in 2021. It has a similar chemical structure to THC, the main psychoactive compound found in cannabis, but with extra hydrogen atoms added. This modification has led to unique pharmacological effects for HxC.
The precise mechanisms of action for HxC are not yet fully understood, but it is believed to interact with cannabinoid receptors, particularly CB1 and CB2, similarly to other cannabinoids in the body. As a result, HxC may produce some effects similar to those of THC, such as euphoria, relaxation, and analgesic properties.
However, there is limited research available on the specific effects of HxC, and more studies need to be performed to fully elucidate the pharmacological properties of this semi-synthetic cannabinoid. Some anecdotal reports suggest that it may differ in potency and duration from THC, but these are not confirmed in scientific literature.
It is important to understand that the use of HxC is still relatively new, and potential risks and side effects are not yet known. Users should be cautious when experimenting with this substance, as there could be hidden dangers related to its consumption. In 2014, the World Health Organization released a report on the potential impact of designer drugs, including cannabinoids like HxC, which highlights the importance of properly documenting and understanding the pharmacological effects, potential benefits, and risks associated with these emerging substances.
In summary, HxC is a semi-synthetic cannabinoid that shares some similarities with THC, but with a distinct chemical structure. Its pharmacological effects are not entirely understood but might involve interactions with cannabinoid receptors in the body. There is a need for more research to fully understand the effects and potential risks associated with HxC, and users should exercise caution when using this substance.
Medical Uses
Hexahydrocannabinol (HHC) is a semi-synthetic cannabinoid closely related to THC, the main psychoactive compound found in cannabis. It is formed by adding extra hydrogen atoms to THC, resulting in a partially hydrogenated compound. The medical uses of HHC are still being researched, and existing knowledge about its effects is limited. However, some potential medical applications can be inferred from its close relationship to THC and other cannabinoids.
- Pain Relief: Cannabinoids like THC and CBD have been shown to offer relief from chronic pain, inflammation, and discomfort associated with various conditions. HHC may share these properties, possibly providing a potent alternative or supplement to traditional pain management treatments.
- Anti-Nausea: THC has long been known to help alleviate nausea and vomiting in individuals undergoing chemotherapy and those with conditions like HIV/AIDS. HHC, due to its similarity to THC, might offer a similar relief from nausea, improving patients’ quality of life.
- Appetite Stimulation: A well-established use of cannabinoids is their ability to stimulate appetite. This can be beneficial for patients with eating disorders, those undergoing chemotherapy, or anyone experiencing a loss of appetite due to medical treatments or conditions. HHC may serve as another option for medical professionals to consider when trying to help patients maintain healthy nutritional intake.
- Neuroprotection: Some studies suggest that cannabinoids may offer neuroprotective effects, helping to slow down the progression of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. While more research is needed to confirm HHC’s specific neuroprotective properties, its similarity to other cannabinoids could make it a potential candidate for further investigation in this area.
It is essential to note that more research is needed to fully understand the medical applications of HHC. As it is a relatively new compound, its safety, efficacy, and potential side effects are not yet entirely understood. However, considering its close relationship to THC and other cannabinoids, HHC offers an interesting area of exploration for the medical and scientific communities.
Contradictions and Side Effects
Hexahydrocannabinol (HxC) is a lesser-known compound found in the cannabis plant. While research on HxC is limited, it is essential to be aware of potential contradictions and side effects. This includes possible interactions with other medications, adverse reactions, and the compound’s legal status.
HxC may interact with certain medications, affecting how they work or causing undesirable side effects. For example, it is believed to inhibit the effectiveness of some pharmaceuticals, potentially raising the risk of negative reactions. If you take prescribed medication, it is vital to consult with a healthcare professional before trying HxC to ensure your safety.
As for side effects, existing research suggests they are generally mild and similar to those of its more famous relative, THC. Possible side effects include:
- Dizziness
- Dry mouth
- Increased heart rate
- Impaired memory and concentration
It is important to note that individual responses to HxC may vary, and some individuals may not experience any side effects at all. However, caution is advised, especially for first-time users or those with a history of adverse reactions to cannabis products.
In terms of legal status, HxC exists in something of a gray area. While it is not explicitly listed as a controlled substance in most jurisdictions, its close relation to THC, a controlled substance, might lead to legal complications in some areas. This could range from restrictions on cultivation and sale to outright bans.
In summary, while Hexahydrocannabinol is not as well-researched as other cannabis compounds, it is crucial to be cautious when exploring its potential benefits and risks. Consulting a healthcare professional and understanding local legal regulations can help ensure a safe and responsible experience with HxC.

Legal Status
Hexahydrocannabinol (HHC), also known as HxC, is a semi-synthetic cannabinoid closely related to THC but with additional hydrogen atoms in its chemical structure1. Its legal status may vary depending on the jurisdiction and the specific isomer of HHC in question.
In the United States, the legal status of HHC is ambiguous and may depend on its isomer, the source of its production, and its level of similarity to THC. As a general rule, substances structurally similar to THC and other Schedule I drugs are considered controlled substances under the Federal Analogue Act2. However, if HHC is derived from hemp, which is defined as any Cannabis sativa plant with less than 0.3% THC, it could arguably fall under the purview of the 2018 Farm Bill that legalized hemp and hemp-derived products at the federal level3.
In many European countries, HHC could potentially be considered a controlled substance under the Convention on Psychotropic Substances or relevant national laws. This is because scheduled substances with structural similarity tend to be regulated in the same manner as the parent compound. It is crucial to note that the specific isomer of HHC and the legal framework in the country in question will greatly influence the legality of possessing or selling H-C.
For those considering the use or distribution of HHC, it is essential to be aware that the legality of this substance may vary significantly across different jurisdictions. Careful consideration of the unique isomer, source, and application of HHC is necessary before diving into its use, as these factors can influence the compound’s legal status.
Research and Future Prospects
Hexahydrocannabinol (HxC) is a relatively lesser-known compound belonging to the vast family of cannabinoids. Research surrounding HxC is still in its infancy. Nonetheless, scientists are beginning to explore the potential therapeutic benefits of this compound.
HxC is structurally distinct from other well-known cannabinoids like THC and CBD. As such, it might exhibit unique properties that could pave the way for new medical applications. For example, early studies have shown that HxC may have anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and neuroprotective effects. These findings have sparked interest in investigating HxC as a potential treatment for conditions such as chronic pain, inflammation, and neurodegenerative diseases.
Shifting regulatory landscapes worldwide have opened up new opportunities for cannabinoid research. As countries continue to decriminalize or legalize cannabis for medical or recreational use, the demand for novel cannabinoid treatments and therapies grows. This is especially true for non-intoxicating cannabinoids like HxC, which could offer medical benefits without the psychoactive effects associated with THC.
Research into HxC, however, is not without its challenges. The compound’s classification as a synthetic analogue of THC in some jurisdictions complicates legal access for researchers. Moreover, the scarcity of HxC makes it difficult to conduct large-scale studies. As scientists learn more about the compound’s unique properties and effects, legislative bodies will need to reconsider its classification to facilitate further exploration.
In summary, HxC is an emerging cannabinoid with untapped potential for future medical applications. As research continues to progress, and as the compound becomes more widely available, HxC’s place within the therapeutic landscape will undoubtedly become clearer.

Conclusion
Hexahydrocannabinol (HHC) is a novel semi-synthetic cannabinoid derived from the more familiar CBD and THC compounds found in cannabis. It has garnered interest in recent years as scientists continue to study its potential therapeutic effects and safety profile.
Research on HHC is still in its infancy, and concrete conclusions regarding its efficacy and safety are yet to be established. However, initial findings reveal some promise, especially in the potential management of chronic pain, inflammation, and other therapeutic applications.
Legal considerations surrounding HHC are complex due to its association with the broader cannabis industry. As regulations evolve, it is crucial for manufacturers, retailers, and consumers to stay informed of the current legal landscape surrounding HHC and other cannabinoids.
In the future, additional research on HHC and closely related semi-synthetic cannabinoids may reveal exciting potential for a wide range of therapeutic applications. As the scientific community gains a better understanding of HHC, it will likely contribute to the ever-growing interest in the medicinal and wellness potential of cannabis and its derivatives.
Hexahydrocannabinol and closely related semi‐synthetic cannabinoids: A comprehensive review
Frequently Asked Questions
How strong is HxC?
Hexahydrocannabinol (HxC) is a synthetic cannabinoid, and its strength can vary depending on the specific chemical structure. It is important to note that synthetic cannabinoids can often be more potent than natural cannabis, with varying and unpredictable effects.
Does HxC get you high?
As a synthetic cannabinoid, HxC can potentially produce psychoactive effects similar to those of natural cannabis. However, the intensity and duration of the high can differ significantly due to the differences in chemical composition.
What are the effects of Hexahydrocannabinol?
The effects of HxC can vary depending on the specific chemical structure, dosage, and individual user’s response. Some potential effects may include euphoria, relaxation, altered perception, increased appetite, and dry mouth. It is important to note that synthetic cannabinoids can also produce adverse side effects, such as anxiety, paranoia, and hallucinations.
Is HxC found in vape cartridges?
HxC may be found in some vape cartridges, particularly those containing synthetic cannabinoids. Users should be cautious when purchasing vape cartridges, as some may contain unregulated or harmful substances.
What are the potential risks of HxC?
The potential risks of HxC can include both short-term and long-term health effects. Short-term risks may include dizziness, nausea, paranoia, and impaired coordination. Long-term use of synthetic cannabinoids like HxC may lead to respiratory issues, addiction, and mental health problems, such as increased risk of depression and anxiety.
Are there any documented experiences on HxC?
Due to the relatively recent emergence of synthetic cannabinoids like HxC, there may be limited documented experiences available. However, users should exercise caution when experimenting with HxC or any other synthetic cannabinoids, as their effects can be unpredictable and potentially hazardous to one’s health.
Footnotes
- Hexahydrocannabinol and closely related semi‐synthetic cannabinoids: A comprehensive review ↩
- Federal Analogue Act – Wikipedia ↩
- 2018 Farm Bill: United States Department of Agriculture ↩







