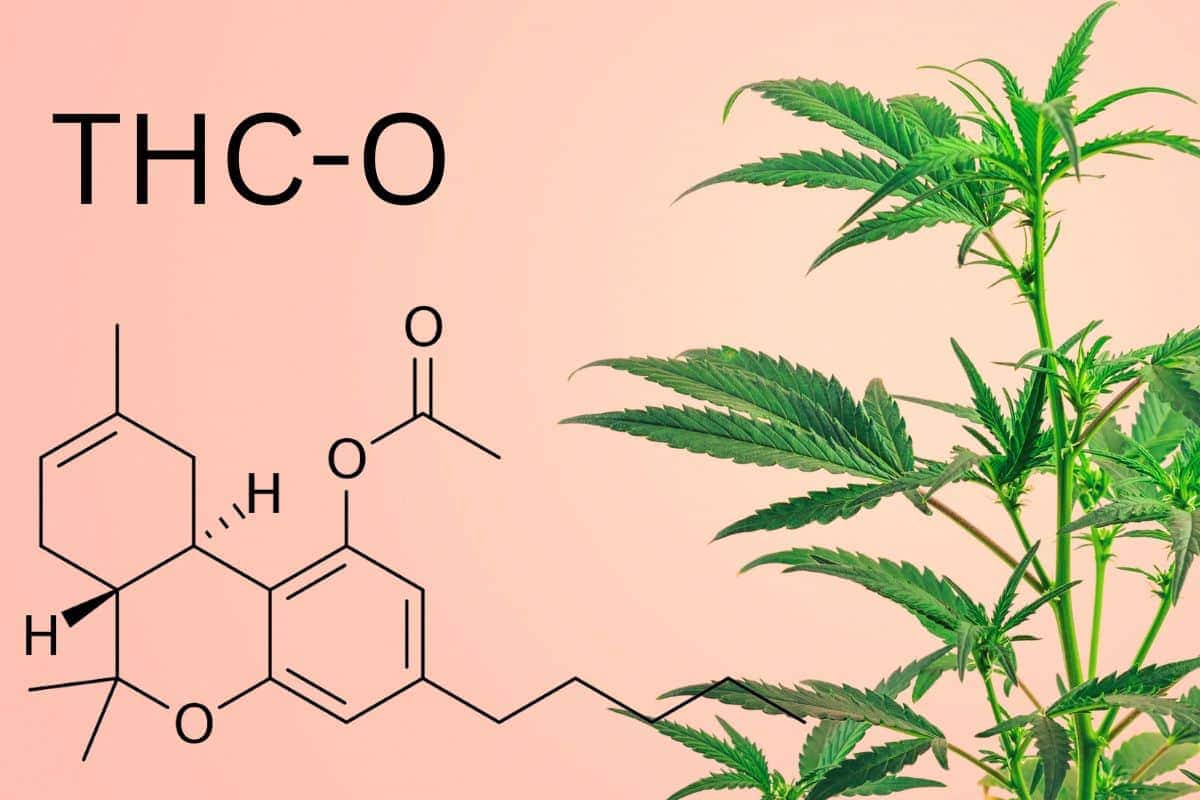
How Long Does THC-O Last in Your System: Duration and Detection Times
Knowing how long THC-O sticks around in your body matters a lot, especially if a drug test looms on the horizon or if you’re on a mission to hit your health targets. Imagine THC-O as the mighty cousin of Delta-9 THC, turbocharged with an acetate twist that cranks up its power. Once it lands in your system, your body gears up to chop it into mini pieces. The speed of this process hinges on a few factors like your usage frequency, its potency, and your body’s composition. Exploring the realm of intense THC-O effects, understanding its journey through your body could save you a ton of stress. Hang tight, and you’ll find out how unlocking this mystery might just flip your world upside down.
Table of contents
Once THC-O enters your system, it may produce effects that are more pronounced than those of other forms of THC. These effects can last for several hours, with the actual psychoactive experience potentially extending beyond that of conventional THC. However, the question of how long THC-O and its metabolites linger in your system is quite complex. It involves understanding both active effects and the window in which THC-O can be detected by various drug tests.
Drug tests look for specific metabolites that result from your body processing THC-O. These metabolites can be identified in blood, urine, saliva, and hair for different lengths of time, ranging from days to even months after consumption, dependent on the testing method used. Accurately estimating how long THC-O will be detectable in your system is challenging, as detection windows can vary significantly from person to person.
Understanding THC-O and Its Properties
THC-O, or tetrahydrocannabinol-O-acetate, is a synthetic cannabinoid derived from hemp. As a compound related to the well-known tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the psychoactive constituent of cannabis, it shares many properties with THC but also has unique aspects. Unlike THC, which occurs naturally in the cannabis plant, THC-O is manufactured in a lab through a chemical process that acetylates THC, altering its molecular structure.
Here’s a brief outline of THC-O’s characteristics:
- Synthesis: Manufactured from legal hemp-derived cannabidiol (CBD).
- Legal status: Often exists in a legal gray area due to its synthetic nature.
- Potency: Believed to be more potent than conventional THC.
In terms of its effects, THC-O is noted for its psychoactive properties, which can be significantly more potent than those of delta-9 THC, the main psychoactive ingredient in cannabis. This heightened potency means that even in small doses, THC-O can produce strong effects. Due to its potency and synthetic origin, there are legal considerations around THC-O that vary by jurisdiction.
When you consume THC-O, it is metabolized by your body, just like other cannabinoids. However, due to its potency and chemical structure, the duration it stays in your system could vary significantly compared to other minor cannabinoids. The time it remains detectable in your body is influenced by various factors, such as your metabolism, dosage, and frequency of use.
It is essential to approach THC-O with caution. After consumption, anticipate a delayed onset of effects compared to natural THC. Because of its synthesized nature, and the lack of extensive research, the full profile of THC-O’s long-term impacts remains to be thoroughly understood.
How THC-O Affects the Body
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Psychoactive Effects | THC-O is reported to be more potent than traditional THC, and users claim it produces intense psychoactive effects. The onset, duration, and intensity may vary among individuals. |
| Binding to Receptors | Like THC, THC-O is believed to interact with the endocannabinoid system (ECS) by binding to CB1 receptors, primarily found in the central nervous system. This interaction contributes to its psychoactive effects. |
| Potential Side Effects | Users have reported experiences such as altered perception, enhanced sensory experiences, and other intense psychoactive effects. As with THC, potential side effects may include anxiety, paranoia, and dizziness. |
| Dosage and Tolerance | Due to its potency, users may require smaller amounts of THC-O compared to THC to achieve similar effects. Tolerance levels may vary among individuals. |
| Legality | The legal status of THC-O may vary by jurisdiction. As with other cannabinoids, it’s important to be aware of and comply with local laws regarding its possession and use. |
When you consume THC-O, it impacts you by interacting with your body’s endocannabinoid system and can have both short-term and long-term effects on your metabolism and overall health.
Interaction With the Endocannabinoid System
THC-O, a synthetic analogue of THC, significantly affects your endocannabinoid system (ECS). When you consume THC-O, it binds with cannabinoid receptors in your ECS, notably CB1 receptors in the brain, which may lead to more potent psychoactive effects than regular THC. This interaction influences various bodily functions, including mood, memory, and appetite.
Short-Term and Long-Term Effects
Short-Term Effects: Right after you use THC-O, you might experience heightened sensory perception, altered sense of time, and in some cases, anxiety or discomfort. These effects can vary based on your individual metabolism and the dose of THC-O consumed.
Long-Term Effects: Frequent cannabis users, especially those who start at a young age, might experience changes in brain structure related to memory and emotional processing. Prolonged THC-O use has been less studied, but similar caution is advised due to its potency and impact on the central nervous system. It’s important to note that effects may persist longer than anticipated, as THC-O’s presence in the body can be prolonged depending on your metabolic rate.
Factors Influencing THC-O Metabolization
THC-O acetate, commonly referred to as THC-O, is a synthetic cannabinoid that is metabolized by your body uniquely due to a variety of factors, including your genetic makeup, usage habits, and individual lifestyle choices.
Genetic Factors
Your genetics play a crucial role in how rapidly THC-O is metabolized. Variations in your liver enzymes, which are responsible for breaking down cannabinoids, can significantly affect your metabolic rate. If you have a genetic predisposition for faster enzyme activity, THC-O may be metabolized more quickly.
Frequency of Use and Dosage
The frequency of use and the dosage of THC-O you consume are directly linked to the duration it stays in your system. Higher doses and more frequent use can saturate the body’s tissues, leading to a longer detoxification process. Regular users may find that THC-O persists in their system longer compared to occasional users.
Body Composition and Lifestyle
Your body composition and lifestyle also have a substantial impact on metabolizing THC-O. A higher body mass index (BMI) and increased body fat can lead to THC-O being retained in fat cells for extended periods. On the other hand, a healthy diet, consistent exercise, adequate sleep, and good hydration levels can enhance your overall metabolic rate, thus aiding in the elimination of THC-O. Your medication routine can also influence how your body processes cannabinoids.
Detection and Testing for THC-O
When you’re concerned about THC-O’s detectability after exposure, understanding the testing methods and detection windows is critical for both personal knowledge and legal implications.
Drug Testing Methods
Your body processes THC-O differently than it does THC, with various drug testing methods available to detect its presence. The common types of drug tests include:
- Urine tests: These are the most prevalent and can identify metabolites like 11-hydroxy-THC.
- Blood tests: These assess active compounds and are useful shortly after exposure.
- Saliva tests: Less invasive, saliva testing is gaining traction for detecting immediate but short detection windows for THC-O and other cannabinoids.
- Hair tests: These can reveal drug use over a more extended period, reflecting compound accumulation in hair follicles over time.
Each method has its own sensitivity and specificity, affecting how long after exposure THC-O can be detected.
Detection Windows
Detection windows refer to the time frames in which drug tests can detect THC-O or its metabolites in your body. These windows can vary by several factors, such as frequency of use and metabolism.
- Urine: Typically, metabolites can be detected for a longer duration in urine, often several days to weeks.
- Blood: THC-O can be detectable in blood for a shorter period, generally up to 24 hours after exposure.
- Saliva: In case of a saliva test, detection is possible for up to a few hours post-consumption.
- Hair: Metabolites may be detectable in hair for months; however, this method reflects usage over time rather than immediate past use.
It’s important to note that detection times can vary greatly depending on individual factors, and THC-O may have longer detection windows compared to THC due to its unique metabolic process.
Factors Affecting THC-O Detection Times
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Metabolism | Individual metabolism plays a significant role. Faster metabolism may result in quicker elimination of THC-O and its metabolites. |
| Frequency of Use | Regular users may accumulate cannabinoids in their system, leading to longer detection times compared to occasional users. |
| Dosage and Potency | Higher doses or more potent forms of THC-O may take longer to be eliminated from the body. |
| Route of Administration | The method of consumption (e.g., smoking, vaping, ingesting) can influence how quickly THC-O is absorbed and metabolized. |
| Body Fat Percentage | THC-O is lipophilic and can be stored in fat tissues. Individuals with higher body fat percentages may have longer detection times. |
| Hydration Level | Adequate hydration can support the elimination of substances through urine. Dehydration may lead to slower elimination. |
| Metabolites Analyzed | Different drug tests may target specific metabolites. The choice of metabolite for testing can affect the detection window. |
| Individual Variation | Genetics, overall health, and other individual factors contribute to variations in how quickly substances are metabolized and eliminated. |
| Detection Method | Different drug testing methods (urine, blood, saliva, hair) have different detection windows. Urine tests are more common for cannabinoids. |
| Cut-off Levels | Drug tests have cut-off levels, below which results are considered negative. Lower cut-off levels may detect lower concentrations for a longer time. |
| Time Since Last Use | The duration between the last use of THC-O and the time of testing is a crucial factor. Detection times generally decrease as more time elapses. |
| Liver and Kidney Function | The proper functioning of the liver and kidneys is essential for metabolizing and excreting substances from the body. Impaired function may affect detection times. |
Detection times for THC-O in your system are influenced by several specific factors. These include how much and how often you consume, as well as your metabolism rate and lifestyle choices.
Frequency and Dosage Variables
Frequency of Use: The more often you use THC-O, the longer it will stay detectable in your system. Chronic use can lead to accumulation in body fat, resulting in extended detection periods.
- Single Use: Detectable for a shorter period.
- Regular Use: May be detectable for an extended time due to build-up.
Dosage Amount: The amount of THC-O consumed in each session directly influences how long it remains detectable.
- Higher Dosages: Lead to longer detection times.
- Lower Dosages: Are metabolized more quickly, shortening detection times.
Biological and Lifestyle Considerations
Metabolism Rate: A faster metabolism will process THC-O more rapidly, potentially reducing detection times.
Body Mass Index (BMI): Higher BMI can increase detection times since THC-O is lipophilic (fat-soluble) and can be stored in fat cells.
Exercise and Diet: Regular exercise and a healthy diet can boost your metabolism, possibly decreasing detection times.
- Fat-Burning Activities: Can expedite the release of stored THC-O from fat cells.
- Water Consumption: Adequate water intake may assist in elimination, though it does not drastically affect detection times.
Lifestyle: Overall lifestyle choices, including diet, exercise, and water intake, contribute to how quickly your body processes and eliminates THC-O.
Methods to Shorten Detection Times

If you’re looking to reduce the detection time of THC-O in your system, focusing on detoxification, diet, hydration, exercise, and metabolism boosters could be beneficial.
Detox and Diet
To enhance your body’s ability to process and eliminate THC-O, incorporate a healthy diet high in fiber. Foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can support your liver and kidneys, helping to expel toxins more effectively. Additionally, certain foods may upregulate enzymes like CYP3A4, which metabolize THC, potentially shortening detection times.
Hydration and Exercise
Consistently high hydration levels are crucial. Aim to drink ample water to keep your system flushed and facilitate the excretion of THC-O metabolites. Exercise, while maintaining a proper hydration balance, accelerates your body’s natural detoxification processes, as THC is stored in fat cells and burned off during physical activity.
Metabolism Boosters
Stimulating your metabolism can also help clear THC-O more quickly. This can be achieved with a combination of a robust exercise regimen and a balanced diet that includes metabolism-boosting foods like green tea and chili peppers. Remember, while these methods may aid in reducing detection time, they’re not guaranteed to work for everyone due to variations in individual metabolism and body composition.
Different Forms of THC-O Consumption

Consuming THC-O can vary in effects and duration depending on whether you inhale or ingest it, as well as what types of products you use. Each method impacts how quickly you feel the effects and how long they last in your system.
Inhalation vs. Ingestion
Inhalation of THC-O, such as through smoking or vaping, typically results in a more immediate onset of effects. When you inhale THC-O, the compounds are absorbed quickly into your bloodstream through your lungs. The effects can be felt within minutes, but they may not last as long as other methods.
On the other hand, ingestion involves consuming THC-O through products like edibles, which are metabolized by your liver before entering your bloodstream. This process results in a delayed onset of effects — usually 30 minutes to 2 hours after consumption. However, the effects of ingested THC-O can last much longer, often several hours, due to the extended metabolic process.
Edibles, Tinctures, and Topicals
- Edibles: THC-O incorporated into edibles such as gummy treats, baked goods, or beverages offers a discrete and easy-to-dose method. The potency of edibles can vary, so start with a low dose and wait to understand your tolerance.
- Tinctures: Tinctures are liquid extracts that you can take sublingually (under the tongue) for a faster onset than traditional edibles. The effects begin to take place within 15 to 45 minutes, giving you control over your dosing.
- Topicals: THC-O can also be found in various topical forms such as creams and balms. However, topicals are generally used for localized effects and are not typically associated with systemic effects or “high” sensations.
Each delivery method affects how THC-O interacts with your body, so choose the form that aligns with your desired experience and convenience.
Legal and Safety Considerations
When considering THC-O, it’s crucial to understand the legalities that govern its use and the risks associated with unregulated products. These factors directly impact your safety and the potential for legal consequences.
Regulatory Status
THC-O is a synthetic cannabinoid, and its legal status may vary depending on where you live. As of the provided information, the regulatory framework for such substances is often complex due to their classification under cannabis legislation. For example, while the 2018 Farm Bill federally legalized hemp-derived products, this does not automatically mean all THC-O products are legal. Always check your local laws to ensure compliance.
Risks of Unregulated Products
The THC-O market is still emerging, leading to a lack of federal safety standards for products containing this compound. This lack of regulation can mean:
- Quality Assurance: Without oversight, products may contain impurities or inconsistent levels of THC-O.
- Health Risks: Using THC-O might pose health risks, especially without clinical trials or FDA approval to back its safety profile.
- Legal Implications: Unregulated use of THC-O might result in a failed drug test, as it’s a THC analogue, and could thus be problematic in jurisdictions where THC is illegal.
Always approach THC-O with caution, recognizing that “legal” does not always equate to “regulated” or “safe.”
Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding the detection window of THC-O in your system is key to navigating legality and health concerns. Here’s concise, reliable information to guide you.
How long can THC-O be detected in a urine analysis?
THC-O can linger in your system and may be detected in urine for up to several weeks, depending on the frequency of use and metabolic rate.
What is the time frame for THC-O to remain in your bloodstream?
THC-O may remain detectable in your bloodstream for 1 to 2 days following use, but this can vary based on individual factors.
Are there specific tests that can identify THC-O usage?
Yes, specialized drug tests have been developed to specifically detect the presence of THC-O and its metabolites in your body.
What factors influence the duration of THC-O’s presence in the body?
The duration of THC-O in your system is influenced by factors such as dosage, frequency of use, metabolism, and your body’s fat content.
Can occasional THC-O use lead to long-term detection in drug tests?
Occasional use of THC-O may still be detectable in drug tests for a few days to over a week, but is less likely to be identified long-term compared to frequent use.
How does THC-O compare to Delta 8 in terms of detection time in drug screening?
THC-O and Delta 8 have similar detection times in drug screenings, though individual metabolism and the sensitivity of the test may cause variations.