How Many Types of THC Are There? Unveiling the Variants of Tetrahydrocannabinol
THC is the wizard’s brew in marijuana that zips you up to the cosmos. Think you’ve got the scoop on THC? Brace yourself for a shocker! A whole universe of **THC varieties** awaits your discovery. Jump into Cannabinoids 101 for a sneak peek at the assortment of THC flavors brought to life by nature’s touch and the genius of scientists. From the kiss of sunshine to the coolness of the lab, every type of THC whirls in your mind, igniting unique adventures and emotions. Why stay in the dark? You’re on the verge of entering a rainbow spectrum of THC that’ll flip your understanding inside out. Get ready to meet the THC family in an extraordinary way that’ll knock your socks off.
Table of contents
- Understanding THC
- Main Types of THC
- Lesser-Known Variants of THC
- Effects and Benefits
- Legality and Regulation
- THC Consumption Methods
- The Role of the Endocannabinoid System
- Industrial Hemp and THC
- Factors Influencing THC Effects
- THC vs. CBD
- Advancements in THC Research
- Quality and Safety Considerations
- THC in Popular Culture
You might be aware of Delta-9-THC, the most abundant and well-studied form, but several other types like Delta-8-THC and THCa, the non-psychoactive precursor to Delta-9-THC, also play significant roles in the cannabis experience. Additionally, variations such as THCV and synthetic analogs like Spice or K2, which mimic THC’s effects to varying degrees, have been identified. Understanding these different forms is crucial for both consumers and professionals navigating the cannabis industry.
Understanding THC
Tetrahydrocannabinol, commonly known as THC, is the primary psychoactive compound found in the cannabis plant. As an active cannabinoid, THC binds to receptors in your brain and body, producing a range of effects. Your body’s own endocannabinoid system—comprising two main types of receptors, CB1 and CB2—interacts with THC differently depending on which receptor is engaged.
CB1 receptors are primarily found in your central nervous system, responsible for THC’s psychoactive effects, such as euphoria and altered sensory perception. Conversely, CB2 receptors are more abundant in the peripheral nervous system, influencing inflammation and pain.
- Types of THC:
| Form | Description |
| Delta-9-THC | The most prevalent and studied form. |
| Delta-8-THC | Less potent and occurs in smaller amounts. |
| THCa | A non-psychoactive precursor in raw cannabis. |
While Delta-9-THC is the most well-known, other analogs like Delta-8-THC also exhibit psychoactive properties but are typically not as potent. Additionally, when you consume raw cannabis, you’re encountering THCa (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid), which doesn’t produce psychoactive effects until decarboxylated—transformed by heat—to THC.
Understanding THC concentrations is crucial, as they dictate the intensity of the psychoactive effects. Products with higher THC levels might be overwhelming for new users, while experienced individuals might seek these for their stronger effects. With cannabis labeling, it’s easier to gauge the amount of THC you consume, ensuring a safer and more controlled experience.
Main Types of THC
THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis. Understand that THC comes in several forms, each with a unique chemical structure and effects on the human body.
Delta-9 THC
Delta-9 THC is the most well-known form of THC, widely recognized for its psychoactive properties. You will experience euphoria, relaxation, and, in some cases, anxiety after consuming Delta-9 THC. It’s the key compound in cannabis responsible for the ‘high’ associated with marijuana and has been researched extensively for its effects on pain, nausea, and vomiting.
Delta-8 THC
Delta-8 THC is a THC analog with a structure similar to Delta-9 THC, but it’s less potent. It still offers psychoactive effects but is generally considered to produce a mellower experience. Your pain and inflammation may be alleviated with Delta-8 THC, and it can act as an appetite suppressant. Its legal status is somewhat complicated; while it’s a component of cannabis, it can also be derived from federally legal industrial hemp.
Delta-10 THC
With Delta-10 THC, you might feel an energizing effect that can enhance focus and concentration, differing from the more sedating influence of Delta-9 THC. The potency of Delta-10 tends to be lower, and it’s found in much smaller quantities in the cannabis plant. Like Delta-8, Delta-10 THC’s legal status in certain areas derives from it sometimes being produced from industrial hemp.
THCa

Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, or THCa, is the non-psychoactive acidic precursor to Delta-9 THC found in raw cannabis plants. It’s only when THCa undergoes decarboxylation, often through heat, that it converts into psychoactive Delta-9 THC. Understanding THCa is crucial if you’re interested in the properties of cannabis in its raw form, before any heating or combustion.
THCV
Tetrahydrocannabivarin, or THCV, is another cannabinoid with a unique offering. Not only can THCV provide a stimulating high, but it might also suppress your appetite, which could be beneficial for obesity management. Additionally, its potential influence on blood sugar levels is a focus of ongoing research. Unlike the other forms of THC, THCV could aid in elevating mood without as profound psychoactive effects.
Lesser-Known Variants of THC
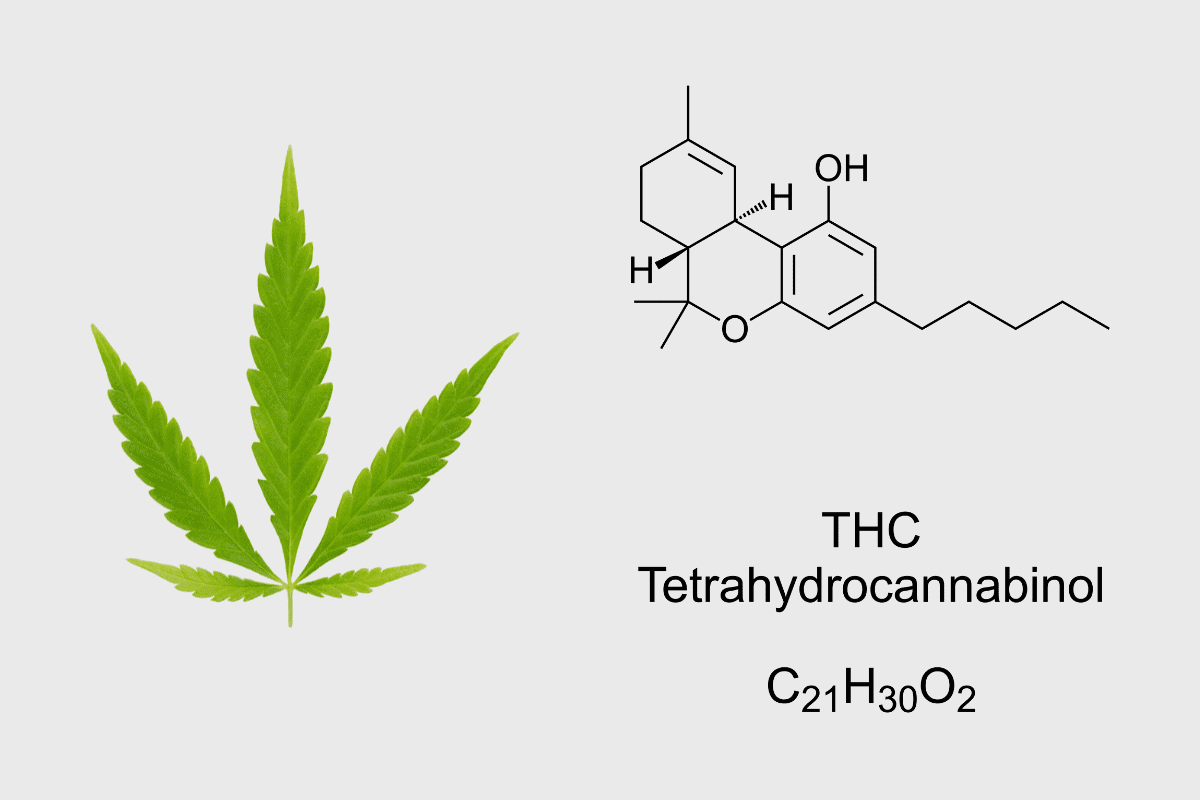
As you deepen your understanding of THC, it’s important to recognize that Delta-9 THC is just one well-known type in a family of compounds. Amongst the various cannabinoids found in cannabis, there are lesser-known variants of THC, each with unique chemical structures and effects. These variants include THC-O, THCP, and THCB—cannabinoids just starting to pique the interest of researchers and consumers alike.
THC-O
THC-O, or THC-O acetate, is a synthetic analogue of THC known for its potency, which is believed to be several times stronger than the more familiar Delta-9 THC. As an acetate ester of THC, its chemical structure allows for potentially more substantial intoxicating effects; however, it’s important to use with caution due to its strength and lack of extensive research.
THCP
In the case of THCP, or tetrahydrocannabiphorol, you are looking at a phytocannabinoid that has been recently discovered and is notable for its high affinity to cannabinoid receptors. THCP’s structure includes a longer alkyl side chain, which might contribute to a potency that’s significantly higher than that of classical THC types, resulting in more pronounced intoxicating effects.
THCB
THCB stands for tetrahydrocannabutol, a naturally occurring phytocannabinoid found in certain strains of cannabis, albeit in much smaller quantities than Delta-9 THC or even the emerging Delta-8 THC. Preliminary findings suggest a difference in intoxicating properties and potency in comparison to Delta-9 THC, making it an interesting subject for further study but remaining largely unstudied and under the radar for many consumers and researchers.
Effects and Benefits

When discussing THC, it’s important for you to understand the various effects and benefits that it offers, which can range from medical to recreational. While THC is known for its psychoactive properties, it also provides therapeutic benefits for some individuals.
Medical Benefits
THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is a key compound in cannabis that offers a range of therapeutic benefits. Specifically, THC has shown promise in:
- Alleviating chronic pain: Studies suggest THC’s efficacy in reducing pain levels.
- Acting as an anti-inflammatory: THC might help in reducing inflammation.
- Offering neuroprotective qualities: Some research points to the potential for THC to help with neurodegenerative diseases.
Psychoactive Properties
THC is responsible for the psychoactive effects associated with cannabis use. When you consume products containing THC, such as edibles, vaping liquids, or via smoking, you may experience:
- Euphoria and relaxation: THC can elicit feelings of well-being and calmness.
- Bliss and a body high: It’s often described as a sense of overall happiness and a tingling sensation throughout the body.
- An increase in appetite, often referred to as the “munchies”.
Potential Side Effects
Like any substance, THC also comes with potential side effects. As you engage with THC through edibles, vaping, or smoking, be aware that you may encounter:
- Nausea and dizziness: Particularly with high doses or first-time use.
- Anxiety and paranoia: Some people report feelings of unease and excessive worry.
- Dry mouth: Commonly referred to as “cottonmouth,” it’s a frequent minor side effect.
Remember that your experience with THC is personal and can vary based on the method of consumption, your tolerance, and the type of product used. It’s crucial to stay informed and approach use with caution.
Legality and Regulation

When exploring the legality and regulation of THC, it’s crucial to differentiate between the various types. THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is the primary psychoactive compound found in cannabis products. It’s essential to understand that not all THC is treated equally under the law.
Federal Law in the United States regards cannabis and its derivatives, including THC, as illegal under the Controlled Substances Act. Yet, despite its federal status, several states have enacted laws permitting the use of medical and recreational cannabis, hence allowing certain types of THC.
However, the introduction of the 2018 Farm Bill changed the legal landscape for hemp-derived products, including those containing delta-8 THC and similar compounds, as long as they contain less than 0.3% delta-9 THC—the most widely recognized and potent form of THC.
Here’s a snapshot of the regulatory status:
- Cannabis-derived THC: Usually illegal federally but may be legal under certain state laws.
- Hemp-derived THC (<0.3% delta-9 THC): Federally legal under the 2018 Farm Bill.
- Synthetic THC: Legal status can vary and often falls into a legal gray area.
It’s clear that while THC and various cannabis products may be legal under certain state laws, they remain illegal under federal law, with specific exceptions related to hemp. If you possess or intend to use products containing THC, it is imperative to consult the laws specific to your locality, as they can differ widely across different jurisdictions. Avoid assuming that legality in one state translates to another. Stay informed to navigate the complex legal landscape surrounding THC.
THC Consumption Methods

When exploring the various ways to consume THC, you’ll find that the route of administration plays a crucial role in how the compound affects you. Here, we’ll break down the common methods:
Smoking: Often the most recognized form of consumption, smoking involves inhaling the combusted flower of the cannabis plant. THC absorption is rapid with this method, leading to almost immediate effects.
- Joints
- Pipes
- Bongs
Vaping: A method that heats cannabis without burning it, releasing THC in a vapor form. It’s considered a less harsh alternative to smoking.
- Dry herb vaporizers
- Oil vape pens
Edibles: Consumable products infused with THC. The onset of effects is delayed as THC is absorbed through your digestive system. Edibles provide a longer-lasting experience with a more pronounced peak. Precise dosage can be more challenging to achieve than with other methods.
- Gummies
- Chocolates
- Baked goods
Topicals and Transdermals: These are creams or patches applied to the skin. While often not psychoactive, they are used for localized relief.
Here’s a simple table summarizing onset and duration:
| Method | Onset | Duration |
| Smoking | Immediate | 1-3 hours |
| Vaping | Immediate | 1-3 hours |
| Edibles | 30 mins – 2 hours | 4-8 hours |
| Topicals | Variable | Variable |
Do note that the THC potency and effects can differ greatly between the different cannabis products and depend on individual tolerance and biological factors.
The Role of the Endocannabinoid System
Your body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a complex cell-signaling system identified in the early 1990s by researchers exploring THC, a well-known cannabinoid. Cannabinoids are compounds found in cannabis. The primary role of your ECS is to maintain homeostasis, a state of balance in your body, by regulating various functions including sleep, mood, appetite, memory, and reproduction.
Components of the Endocannabinoid System:
- Endocannabinoids: These are molecules your body produces that are similar to cannabinoids but produced by your own body.
- Receptors: The two main receptors are:
- CB1 receptors, mostly found in the central nervous system.
- CB2 receptors, mainly located in the peripheral nervous system, especially immune cells.
Endocannabinoids can bind to either receptor, and the resulting effects depend on where the receptor is located and which endocannabinoid it binds to. For example, endocannabinoids might target CB1 receptors in a spinal nerve to relieve pain. Others might bind to a CB2 receptor in your immune cells to signal that your body is experiencing inflammation, a common sign of autoimmune disorders.
Your endocannabinoid system is key in regulating a range of functions and processes. It plays a part in regulating neurotransmitters, chemical messengers that carry signals between nerve cells or from nerve cells to other target cells. By influencing the activity of neurotransmitters, the ECS can help modulate responses to stress and trauma, thereby possibly affecting conditions like anxiety or depression.
Understanding the sophisticated ways in which the ECS facilitates interaction between the different biological systems in your body can lead to potential therapeutic applications, which leverage the regulatory functions of this system.
Industrial Hemp and THC

When you’re looking into the THC content in hemp versus Cannabis sativa plants cultivated for medical or recreational purposes, it’s crucial to understand the distinctions. Industrial hemp is a type of Cannabis sativa that differs significantly from its high-THC counterparts.
Firstly, THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is the primary psychoactive compound found within the cannabis plant that produces the “high” sensation. However, industrial hemp is characterized by its low THC content. By legal standards, notably those detailed in the 2018 Farm Bill, hemp must contain no more than 0.3% THC on a dry weight basis. This minimal amount is not sufficient to produce psychoactive effects.
| Cannabis Type | THC Content |
| Industrial Hemp | <= 0.3% THC |
| Marijuana | > 0.3% THC (varies) |
Different types of THC, such as delta-9-THC, delta-8-THC, and others, are found in varying concentrations within the cannabis plant. Industrial hemp typically contains delta-9-THC, but at levels that comply with legal thresholds and are essentially non-intoxicating.
Your understanding of industrial hemp’s THC content should extend to its use case. Because of the low THC level, industrial hemp is primarily grown for non-drug uses such as textiles, construction materials, and sometimes for CBD production. Contrastingly, cannabis varieties grown for recreational or medical purposes are bred to increase their THC content, thus altering their eligibility under the Farm Bill’s guidelines for legal cultivation and sale.
Factors Influencing THC Effects
When you consume THC, several factors can influence its effects on your body. Understanding these can help you gauge how THC might affect you personally.
1. Body Weight and Composition: Your body weight and fat percentage can impact how THC is absorbed and metabolized. Generally, individuals with higher body fat may experience more prolonged effects as THC is lipophilic and tends to be stored in fat cells.
2. Metabolism: Your metabolic rate determines how quickly your body processes THC. A faster metabolism breaks down THC more swiftly, potentially shortening the duration of its effects.
3. Liver Function: Your liver plays a crucial role in metabolizing THC. Variations in liver enzymes can affect how you feel after consumption. Some people may metabolize THC faster due to their liver’s enzyme levels, affecting the intensity and duration of the drug’s psychoactive effects.
4. Tolerance: Regular use can lead to increased tolerance, meaning you’ll need higher doses of THC to achieve the same effect. Over time, your body becomes more adept at processing THC, which can diminish its impact.
5. Delivery Method: The way you introduce THC into your system impacts how it affects you. Smoking or vaping typically results in faster onset of effects, while edibles take longer to process but the effects may last longer.
| Factor | Influence on THC Effects |
| Body Weight | Affects absorption and metabolization pace |
| Metabolism | Determines the speed of processing THC |
| Liver Function | Influences intensity and duration |
| Tolerance | Higher tolerance reduces sensitivity to THC |
| Delivery Method | Affects onset and duration of effects |
When considering THC use, it’s important to factor in these aspects to predict its potential effects on your system.
THC vs. CBD

Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) are two primary cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant. While both are naturally occurring compounds, they have distinct properties and effects on your body.
THC is well-known for its psychoactive effects – it’s the component that produces the ‘high’ associated with cannabis use. In contrast, CBD is non-psychoactive, which means it doesn’t cause a high, making it an appealing option for those seeking the therapeutic benefits of cannabis without the altered state of mind.
Concerning their effects on anxiety and relaxation:
- THC can induce relaxation but may also lead to increased anxiety in some individuals.
- CBD is commonly linked to reducing anxiety and is being studied for its potential as an anxiolytic (anxiety-reducing agent).
The two cannabinoids are often considered for their therapeutic potential. THC has been used to alleviate symptoms such as pain, nausea, and insomnia. However, CBD has been researched for a broader range of therapeutic applications, including anti-inflammatory effects and neuroprotective properties.
Legality also differentiates THC and CBD. THC is still considered a Schedule I drug under federal law in the United States, with legality varying by state. Meanwhile, CBD derived from hemp, containing less than 0.3% THC, is federally legal following the 2018 Farm Bill.
In various studies, it has been suggested that CBD may modulate the effects of THC. Some propose that a balance between THC and CBD may maximize cannabis’ benefits while minimizing its potential adverse effects. This synergistic interaction is an ongoing area of research.
| Cannabinoid | Psychoactive | Anxiety | Relaxation | Legality |
| THC | Yes | Varies | Yes | Varies |
| CBD | No | Reduced | Yes | Federally Legal |
Understanding the differences between THC and CBD is crucial when considering cannabis for therapeutic use. Each has unique characteristics, and their effects can vary widely from person to person.
Advancements in THC Research

Recent progress in the field of cannabis science has uncovered a more intricate picture of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the psychoactive component in cannabis. Your understanding of THC’s impact on the human body is being refined by the efforts of researchers who are dedicated to elucidating the compound’s nuanced effects.
Clinical trials are imperative for gauging the safety and efficacy of THC in various therapeutic applications. For instance, a study on cannabis intoxication showcased advancements in identifying acute cannabis use, helping to reassure driving safety concerns. The development of such detection methods underscores the commitment to public safety within the sphere of THC research.
Researchers have also begun to explore beyond traditional THC, probing the effects of novel cannabinoid compounds. The investigation into cannabinoid designer drugs such as synthetic cannabinoids aims to comprehend their place within the broader landscape of psychoactive substances, shifting the scientific perspective on what constitutes THC and its variants.
Forward-thinking studies in biotechnology are playing a pivotal role in how you conceive of THC utilization. Recent advances discussed in a comprehensive review focus on genetic engineering and cultivation practices to optimize the yield and potency of THC-producing plants. The implications for medical and recreational use are considerable, shaping future prospects for cannabis biotechnology.
In the realm of cancer research, THC is being tested for its potential anti-tumor effects. Diving into the molecular level, studies have revealed that THC may impede tumor growth, opening up promising avenues for cancer treatment strategies.
The landscape of THC research is vast and continually evolving. As you look ahead, stay informed about the latest discoveries that are shaping the understanding and application of this multifaceted molecule.
Quality and Safety Considerations
When assessing the quality and safety of THC in cannabis products, it’s imperative to consider the presence of contaminants and the thoroughness of lab testing. THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is the main psychoactive compound in cannabis, with several analogs like Delta-9-THC and Delta-8-THC, which deliver varying effects and potency.
Quality Assurance: To ensure you receive a product that is both effective and safe, look for goods that adhere to rigorous quality assurance practices. This includes:
- Standardized Lab Testing: Reliable lab testing for potency and purity is non-negotiable. Tests should measure not just THC levels but also the presence of pesticides, molds, and heavy metals.
- Certification Standards: High-quality products often follow Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) or are certified by third-party organizations.
Safety Protocols:
- Contaminant Screening: Regular screening for contaminants is crucial as they can pose significant health risks.
- THC Potency: Understanding the level of THC is important for dosing and avoiding unwanted side effects.
- Label Accuracy: The product should have accurate labeling that reflects the lab test results, providing confidence in the THC content and safety of the product.
Your health is paramount. Always opt for cannabis products from reputable sources that provide clear and transparent information about their lab testing and quality control processes.
THC in Popular Culture

THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is widely recognized for its central role in the cultural representation of cannabis. Your understanding of marijuana within popular culture is often shaped by music, film, and influential personalities who have openly celebrated its recreational use.
For instance, rap and hip-hop artists such as Snoop Dogg have been vocal about their relationship with cannabis, contributing to both its mainstream exposure and shifting social perceptions. You’ll find that Pop Culture’s Influence on Recreational Marijuana Use & Legislation elaborates on this cultural phenomenon.
The entertainment industry has followed suit, with television shows like “High Maintenance” reflecting the normalization of marijuana in daily life. This portrayal links back to the recognition that cannabis, and therefore THC, is becoming less stigmatized.
Below, you can find how the THC content of cannabis is portrayed across various cultural mediums:
| Medium | Portrayal Context |
| Music | Lyrics and videos often celebrate THC’s recreational effects. |
| Television | Shows depict everyday use, influencing perception and acceptance. |
| Film | Movies feature characters engaging in recreational use. |
| Internet Memes | Humorous content online frequently references THC and cannabis. |
| Celebrity Advocacy | Public figures openly discuss their use, impacting legislation and societal views. |
The dialogue around THC in popular culture is complex and intertwined with debates on legislation and health. As you watch films, listen to music, or engage with media, you are experiencing the evolving narrative around cannabis and its psychoactive component, THC.
Frequently Asked Questions
In this section, you’ll find clear answers to common questions about the various types of THC, their effects, legality, and characteristics.
How do the effects of various THC types differ?
Different types of THC, such as Delta-9, Delta-8, and THCP, exhibit varying levels of potency and effects. For instance, Delta-9 is known for its strong psychoactive effects, while Delta-8 tends to offer a milder experience.
What distinguishes THCP from other THC compounds?
THCP is distinguished by its longer alkyl side chain, which allows it to bind with the CB1 receptor of the endocannabinoid system more effectively than the more common Delta-9 THC, potentially making it significantly more potent.
Can you explain the differences between legal and illegal THC compounds?
The legality of THC compounds often depends on their source and concentration. For example, Delta-9 THC is illegal in many places if derived from marijuana in concentrations above 0.3%, while the same compound derived from hemp with lower concentrations may be legal.
What are the known forms of THC found in cannabis products?
Cannabis products can contain various forms of THC, including Delta-9 THC, which is the most abundant in cannabis plants, as well as Delta-8 THC and the newly discovered Delta-10 THC, both of which occur in much smaller amounts.
In what ways do cannabinoids’ effects vary?
Cannabinoids like THC and CBD have different effects due to their distinct chemical structures and interactions with the endocannabinoid system. THC typically induces psychoactive effects while CBD is non-intoxicating and may offer therapeutic benefits.
What are the primary kinds of THC and their respective properties?
The primary kinds of THC include Delta-9 THC, known for its psychoactivity, Delta-8 THC which offers a more subdued effect, and THCP that might provide an even more intense experience due to its strong affinity for cannabinoid receptors.