How Long Does THCa Stay in Your System: Understanding Detection Times
Cracking the code on how long THCa likes to hang out in your system is a big deal if you’ve got a drug test coming up for a new gig or if you’re trying to stay on the right side of the law. Think of THCa as THC’s chill cousin that doesn’t buzz you up. But get this: when you eat or touch fresh cannabis, THCa sneaks into your bloodstream. This sly guest isn’t aiming to party in your noggin, but with a little twist, it might just morph into THC. Smart cookies can learn heaps about your pot experiences by measuring this. Let’s jump into the THCa rabbit hole and uncover how it plays a sneaky game of hide and seek in your body. Gear up for some jaw-dropping insights that might just flip the script on your upcoming drug test!
The duration that THCa remains detectable in your system varies based on several factors, including the frequency of cannabis use, metabolic rate, and the type of test used for detection. Generally, THCa can be found in hair follicles for longer periods compared to blood or urine. In certain cases, you might be exposed to THCa without direct consumption, for instance, through contact while handling cannabis plant material.
Table of contents
Whether you consume THC directly or are exposed to THCa, it’s crucial to have accurate information about how these compounds interact with your body and how long they can be identified by testing methods. While THCa might not be the primary target of drug tests, understanding its presence and conversion to THC can help you navigate situations where cannabis consumption has legal or professional repercussions.
Understanding THC and THCa

In the exploration of cannabis compounds, discerning between THC and THCa is pivotal for understanding their effects on your body.
Cannabis and Its Compounds
Cannabis contains over a hundred cannabinoids, but tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCa) are among the most significant. THC is the primary psychoactive component of cannabis, responsible for the “high” sensation. On the other hand, THCa is a non-psychoactive precursor to THC, found in the raw plant. When cannabis is heated, through smoking or cooking, THCa undergoes decarboxylation and converts into THC.
- THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol)
- Psychoactive: Yes
- Found in: Heated cannabis products
- Effects: Euphoria, relaxation, altered time perception
- THCa (Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid)
- Psychoactive: No
- Found in: Raw cannabis plant
- Effects: Potential therapeutic benefits without the high
Cannabinoid Safety: While both compounds interact with the endocannabinoid system, their effects on safety and health vary due to their different properties.
Psychoactive Effects
The psychoactive effects of cannabis are primarily attributed to THC. It binds to cannabinoid receptors in your brain, altering your mood, cognitive functioning, and perception. Conversely, THCa is non-psychoactive and doesn’t produce these effects. Instead, it has been researched for potential neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory properties, contributing to the therapeutic benefits of hemp and cannabis without intoxication.
- Binding to the Endocannabinoid System:
- THC: Binds with CB1 receptors, causing psychoactive effects.
- THCa: Does not bind efficiently, thus no psychoactive effects.
Understanding these nuances helps you make informed decisions about your consumption and the potential impact on your body and mind.
Metabolism of THC and Detection

When you consume cannabis, the active components, including THC, undergo a complex breakdown process in your body involving your liver and other tissues. The detection of these substances can vary depending on several factors.
Drug Metabolization Process
When you ingest cannabis, the THC is quickly absorbed into your bloodstream. Your liver plays a crucial role as it metabolizes THC into a variety of metabolites, the most notable being THC-COOH. This process is influenced by factors such as body fat and frequency of use, since THC is fat-soluble and can accumulate in fatty tissues.
- Absorption: THC enters your bloodstream, reaching peak levels quickly.
- Metabolism: Primarily occurs in the liver, transforming THC into various metabolites.
- Distribution: Metabolites are carried to bodily tissues, with some, like THC-COOH, storing in fatty tissues.
- Elimination: Over time, metabolites are excreted through urine and feces.
THC and THC Metabolites
- Presence in Bodily Fluids: Detection of THC and its metabolites can be performed through analysis of your blood, urine, saliva, and even hair. THC is detectable in your saliva shortly after use due to oral mucosa contamination, with metabolite THC-COOH appearing at low concentrations. Urine testing is more focused on THC metabolites rather than THC itself.
- Factors Influencing Detection Times:
- Frequency of Use: The more frequent the usage, the longer THC metabolites tend to remain in your system.
- Body Fat: As THC is fat-soluble, individuals with higher body fat may retain cannabinoids longer, affecting detection times.
- Decarboxylation: THC undergoes decarboxylation to become active, and its metabolites are also subject to this process, which is critical for detection.
- Detoxification: Detox processes aim to expedite elimination, but the efficacy can vary significantly from person to person.
Understanding these mechanisms can help you comprehend how long THC and its metabolites can linger in your system and the factors that affect their detection and elimination.
Factors Affecting Drug Test Results
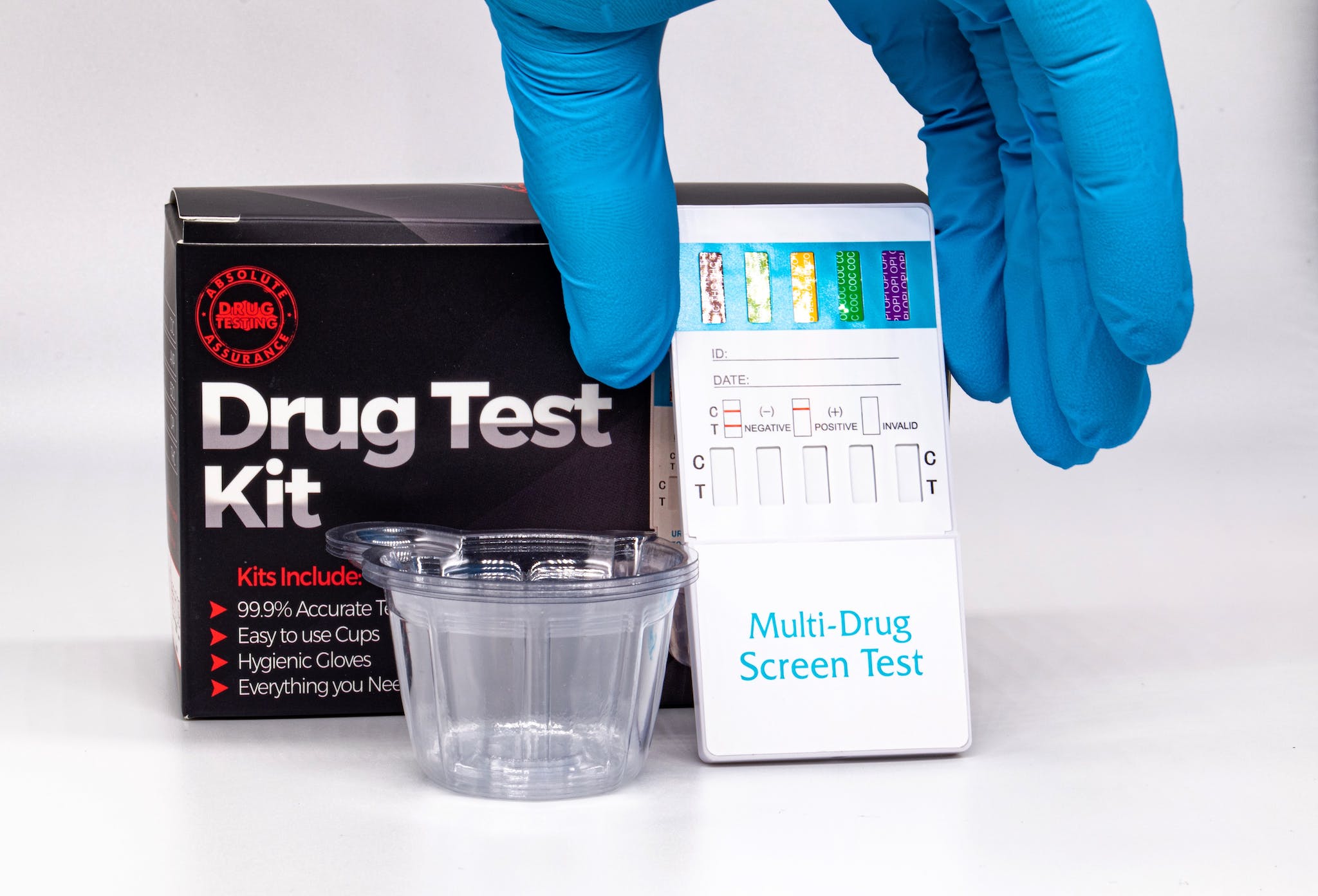
When considering how long Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCa) stays in your system, various factors come into play. These can affect the results of drug tests, particularly urine drug tests, which are commonly used to detect cannabis use. Understanding these variables is crucial as they govern the detectability of THC, THCa’s psychoactive counterpart, following marijuana consumption.
Frequency of Cannabis Use
The more often you use cannabis, the longer THC is likely to remain detectable in your system. Chronic heavy use can lead to accumulation in body fat, which then slowly releases back into your bloodstream over time. On the other hand, occasional users may find that THC clears from their system more quickly.
Body Mass and Composition
Your body mass index (BMI) and body fat percentage can affect the duration THC and THCa are detectable. Individuals with higher body mass and fat may experience a longer retention of these compounds, as THC is lipophilic, meaning it binds to fat cells.
- Exercise: Regular exercising may help to reduce body fat and, consequently, the amount of THC stored.
- Alcohol: Consumption of alcohol could potentially affect your body composition and how it metabolizes THC.
Hydration and Diet
Staying properly hydrated and maintaining a well-balanced diet can influence how quickly your body eliminates THC. A higher rate of hydration can result in more dilute urine, which may affect the concentration of THC metabolites detected in a urine drug test.
- Dietary Choices: Foods that help boost metabolism, such as those rich in fiber, can aid in the quicker passage of THC through your system.
Metabolic Rate
A faster metabolism means your system processes substances quicker, which could reduce the detection window for THC. General health and fitness levels often correlate with metabolic rate; better overall health usually equates to a faster metabolism.
Individual factors such as genetics also play a role, which means that the rate at which your body processes THC is unique to you.
Types of Drug Tests for Cannabis

When checking for the presence of cannabis in your system, various types of drug tests may be employed, each with their own detection windows and testing methods. These tests target compounds like THC and its precursor THCa, which could indicate recent or past cannabis use.
Blood and Saliva Testing
Blood tests are typically used to identify active THC in your bloodstream. This method has a relatively short detection window, as THC is quickly metabolized. The presence of THC in blood tests can usually be seen within seconds to a few hours after usage. Blood tests are often used in contexts such as impaired driving investigations due to their ability to show recent use.
Saliva testing is another form of testing that is increasingly used for its non-invasiveness and because it can detect recent use. THC can appear in your saliva within minutes after use and can potentially be detected for up to 24 hours. Detection times may vary based on frequency of use and individual metabolism.
Urine and Hair Testing
Urine tests are the most common form of drug testing, especially for employment. These test for the presence of THC metabolites, not THC itself. A positive urine test means that your body has recently processed these substances. Urine drug testing can typically detect cannabis use from a few days to several weeks after exposure, depending on your usage habits and physiology.
Hair testing, which examines your hair follicles, can identify cannabis usage over a longer period. It measures the metabolites that have entered the hair follicles through the bloodstream. Cannabis can be detected for up to 90 days in hair testing, but it might not capture recent use since it takes time for metabolites to show up in hair. The detection of cannabis via hair isn’t as affected by temporary abstinence before the test, making it a choice for understanding long-term substance use.
Impact of Consumption Methods on Detection

The detection window of THCa in your system can vary significantly depending on whether you smoke, consume edibles, vape, or use other methods of cannabis consumption. Factors such as absorption rates and the potency of the product influence how long THCa remains detectable.
Smoking versus Edibles
When you smoke cannabis, THCa is rapidly converted to THC due to the high temperatures involved. Smoking leads to a quick onset of effects as THC enters your bloodstream directly through the lungs. This can result in a shorter detection window in body fluids, as THC is metabolized relatively fast. In contrast, eating edibles involves ingesting THCa, which then undergoes a more prolonged conversion process in the digestive system before entering the bloodstream. This indirect route means that THCa, as well as the psychoactive THC, can be detectable for a longer period as they are metabolized more slowly.
Vaping and Alternative Methods
Vaping, a method that also involves inhalation, typically results in a detection timeline similar to smoking. The heat from vaping converts THCa to THC, leading to rapid absorption and a shorter detection span. However, alternative methods such as tinctures or topical applications can introduce cannabinoids like THCa into your system through different absorption pathways. For instance, sublingual absorption via tinctures can lead to detectability patterns that differ from both smoking and ingesting due to the direct entry of cannabinoids into the bloodstream through mouth tissues. The method of consumption substantially influences how long THCa can be traced in your body.
Interference and Drug Test Accuracy
When examining how long THCa stays in your system, you must understand that accuracy of drug tests can be influenced by various substances and conditions, which may produce false positives. Identifying and mitigating these interferences is crucial for improving test precision.
Influences Leading to False Positives
Nitrite and other substances may interfere with the accurate detection of cannabinoids, like THCa and delta 9 THC, in your system. Research suggests that a lack of recovery of the ions of 9-THCa during GC-MS confirmation can be a problem. For instance, particular legal medications or foods consumed could potentially lead to a false positive result. This underscores the importance of considering external factors that could influence test outcomes when interpreting results of a THC test. Learn more from the study on clinical interpretation of drug testing results.
Improving Test Precision
Accurate mass spectrometry and HNMR (Hydrogen-1 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) techniques have shown promise in correctly identifying THC-related compounds, such as THCa, thus reducing the likelihood of matrix interference. To improve the sensitivity and reliability of drug tests, especially roadside screenings for cannabis intoxication, reducing endogenous interferences is vital. The ideal test should be able to distinguish between THC and hemp-derived THC, which may be present due to the legal consumption of hemp products. Read about the two-dimensional gas chromatography technique used to detect THCa and improve sensitivity.
State Laws and Regulations

When considering how long THCa stays in your system, it’s important to understand that various states have differing regulations surrounding marijuana use. These policies can influence not only the legality of cannabis but also how its consumption is tested and penalized.
Variety in Drug Policy by State
In the United States, the legality of cannabis, which includes marijuana and its cannabinoid components like THCa and THC, varies considerably from one state to another. For instance, California allows cannabis for both medical and recreational use, whereas Idaho prohibits it in all forms. It’s essential for you to be aware of your state’s specific legislation as it will dictate the legal implications of marijuana in your system.
Each state that permits marijuana use also implements its own testing methods to determine if individuals are under the influence, especially in contexts such as driving or workplace scenarios. While some states rely on blood tests, others may utilize urine or saliva tests. It’s crucial for you to know that these tests can detect not just THC but also THCa, which can be an indicator of recent cannabis use.
Remember: even if you’re in a state where marijuana is legal, you can still be subject to drug tests for employment or legal purposes. The methods used and the duration cannabis can be detected in your system vary by state, so be familiar with your local laws and regulations concerning pot, weed, or other substances.
Health Implications of Cannabis Use
Cannabis has diverse effects on your health, ranging from immediate psychoactive effects to long-term medicinal benefits. Understanding the short-term and potential long-term implications is crucial for making informed decisions about its use.
Short-Term and Long-Term Effects
Short-term effects of cannabis use can include altered senses, changes in mood, impaired body movement, difficulty with thinking and problem-solving, and impaired memory. Acute high doses can lead to acute psychosis, which includes hallucinations and paranoia.
On the other hand, long-term effects may vary based on your frequency of use and the quantities consumed. Research indicates possible correlations between chronic marijuana use and an increased risk of mental health issues in some individuals, including disorders like schizophrenia.
Medical Considerations
Cannabis contains therapeutic compounds that can be utilized for medicinal purposes. It has been studied for its effectiveness in treating chronic pain, and there is evidence supporting its use in conditions like arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and Parkinson’s disease. These compounds are believed to help manage pain and reduce inflammation.
Moreover, some cannabinoids have been shown to have antioxidant properties, which could potentially protect against cardiovascular diseases. However, additional research is necessary to fully understand their medicinal benefits and the implications of long-term use.
Strategies for Detoxification
When considering the elimination of tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCa) from your system, detoxification strategies can involve natural methods or the use of specifically designed supplements and commercial products. These approaches focus on enhancing your body’s ability to metabolize and expel substances, with an emphasis on maintaining hydration, supporting overall health, and targeting fatty tissues where metabolites may accumulate.
Natural Detox Methods
- Hydration: Ensuring adequate water intake is crucial for detoxification. It helps to dilute substances in your body and facilitates their excretion through urine. Aim for at least 8-10 glasses of water daily to support kidney function and toxin elimination.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can increase metabolism and promote the burning of fatty tissues, where THCa metabolites may reside. Activities like running, swimming, or cycling can be effective for this purpose.
- Overall Health: A well-balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber supports your body’s natural detox pathways. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains in your meals to bolster these processes.
Supplements and Commercial Products
- Herbal Supplements: Certain herbs, such as milk thistle or dandelion root, are touted for their detoxification properties. They are believed to support liver function, a primary organ responsible for metabolizing compounds like THCa.
- Supplements: There are commercial supplements designed to aid in detoxification. These often contain a blend of vitamins, minerals, and natural diuretics to accelerate the body’s eliminatory processes. However, be wary of claims and always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
Remember, while detox methods can support the body’s natural processes, they are not guaranteed to eliminate THCa instantly and results can vary based on individual factors like metabolism and frequency of use.
Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding the duration of THCa’s presence in your system and its detectability is crucial if you are undergoing drug testing. Here are some detailed answers to common queries regarding THCa.
What is the detection window for occasional THCa use in a drug test?
For occasional THCa users, the detection window in drug tests can range from a few days up to a week. The exact time frame depends on several factors, including your metabolism and the amount consumed.
How long does it take for frequent users to eliminate THCa from their urine?
Frequent users may expect THCa to remain detectable in their urine for up to 30 days or even longer, depending on usage patterns and individual metabolism.
Can consuming Delta 8 result in a positive drug test for THCa?
Yes, consuming Delta 8 can potentially result in a positive drug test for THCa, as it is a metabolite that might be detected by certain tests designed to find THC derivatives.
What does a urine THC concentration of 200 ng/ml indicate?
A urine THC concentration of 200 ng/ml indicates a relatively recent use of cannabis. This level is above the typical cutoff used in many drug testing protocols.
For a urine test to indicate below 15 ng/ml, how much time should pass?
For your urine test to indicate below the standard cutoff of 15 ng/ml, it typically requires a few days to several weeks abstaining from cannabis, depending on your usage habits and body metabolism.
What are the implications of a high level of carboxy-THC found in urine?
A high level of carboxy-THC found in urine suggests significant cannabis consumption. This metabolite is the result of your body breaking down THC and can be used as an indicator of usage amount and frequency.